Neural Circuitry-Neurogenesis Coupling Model of Depression
- PMID: 33671109
- PMCID: PMC7957816
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052468
Neural Circuitry-Neurogenesis Coupling Model of Depression
Abstract
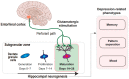
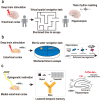
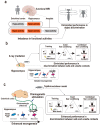
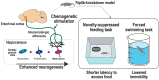
Depression is characterized by the disruption of both neural circuitry and neurogenesis. Defects in hippocampal activity and volume, indicative of reduced neurogenesis, are associated with depression-related behaviors in both humans and animals. Neurogenesis in adulthood is considered an activity-dependent process; therefore, hippocampal neurogenesis defects in depression can be a result of defective neural circuitry activity. However, the mechanistic understanding of how defective neural circuitry can induce neurogenesis defects in depression remains unclear. This review highlights the current findings supporting the neural circuitry-regulated neurogenesis, especially focusing on hippocampal neurogenesis regulated by the entorhinal cortex, with regard to memory, pattern separation, and mood. Taken together, these findings may pave the way for future progress in neural circuitry-neurogenesis coupling studies of depression.
Keywords: depression; entorhinal cortex; hippocampus; memory; mood; neural circuitry; neurogenesis; pattern separation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest relevant to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Entorhinal Cortex and Adult Neurogenesis in Major Depression.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 29;22(21):11725. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111725. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural stem cell of the hippocampus: development, physiology regulation, and dysfunction in disease.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014;107:183-206. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416022-4.00007-X. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24439807 Review.
-
The Role of Neural Plasticity in Depression: From Hippocampus to Prefrontal Cortex.Neural Plast. 2017;2017:6871089. doi: 10.1155/2017/6871089. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Neural Plast. 2017. PMID: 28246558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Born this way: Hippocampal neurogenesis across the lifespan.Aging Cell. 2019 Oct;18(5):e13007. doi: 10.1111/acel.13007. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Aging Cell. 2019. PMID: 31298475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Depletion of adult neurogenesis exacerbates cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease by compromising hippocampal inhibition.Mol Neurodegener. 2017 Sep 8;12(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0207-7. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 28886753 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Microbial-Based Approach to Mental Health: The Potential of Probiotics in the Treatment of Depression.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 13;15(6):1382. doi: 10.3390/nu15061382. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Entorhinal Cortex and Adult Neurogenesis in Major Depression.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 29;22(21):11725. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111725. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of neurogenesis and cognition through intranasal co-delivery of galanin receptor 2 (GALR2) and neuropeptide Y receptor 1 (NPY1R) agonists: a potential pharmacological strategy for cognitive dysfunctions.Behav Brain Funct. 2024 Mar 28;20(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12993-024-00230-5. Behav Brain Funct. 2024. PMID: 38549164 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive Dysfunction in Unipolar Depression.Indian J Psychol Med. 2024 Jul 31:02537176241259683. doi: 10.1177/02537176241259683. Online ahead of print. Indian J Psychol Med. 2024. PMID: 39564278 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Cognitive Functions and Neuronal Growth through NPY1R Agonist and Ketamine Co-Administration: Evidence for NPY1R-TrkB Heteroreceptor Complexes in Rats.Cells. 2024 Apr 12;13(8):669. doi: 10.3390/cells13080669. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38667284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lopez A.D., Mathers C.D., Ezzati M., Jamison D.T., Murray C.J. Global Burden of Disease and Risk Factors. The World Bank; Washington, DC, USA: 2006. - PubMed
-
- Hay S.I., Jayaraman S.P., Truelsen T., Sorensen R.J., Millear A., Giussani G., Beghi E. GBD 2015 disease and injury incidence and prevalence collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015 (vol 388, pg 1545, 2016) Lancet. 2017;389:E1. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

