Inhibitory Effect of a Rosmarinic Acid-Enriched Fraction Prepared from Nga-Mon (Perilla frutescens) Seed Meal on Osteoclastogenesis through the RANK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33671207
- PMCID: PMC7923133
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10020307
Inhibitory Effect of a Rosmarinic Acid-Enriched Fraction Prepared from Nga-Mon (Perilla frutescens) Seed Meal on Osteoclastogenesis through the RANK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
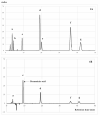
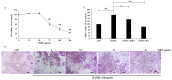
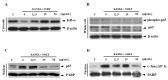
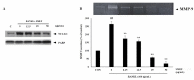
The aim of this study is to determine antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities relating to the antiosteoporosis effects of various perilla seed meal (PSM) fractions. The remaining waste of perilla seed obtained from cold oil compression was extracted with 70% ethanol and sequentially fractionated according to solvent polarity with hexane, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, and water. The results indicated that the seed-meal ethyl acetate fraction (SMEF) exhibited the highest antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, and rosmarinic acid (RA) content. The signaling pathways induced by the receptor activator of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) ligand (RANKL) that trigger reactive oxygen species (ROS) and several transcription factors, leading to the induction of osteoclastogenesis, were also investigated. The SMEF clearly showed attenuated RANKL-induced tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)-positive multinucleated osteoclasts and TRAP activity. A Western blot analysis showed that the SMEF significantly downregulated RANKL-induced NF-κB, AP-1 activation, and the nuclear factor of activated T-cell 1 (NFATc1) expression. SMEF also suppressed RANKL-induced osteoclast-specific marker gene-like MMP-9 using zymography. Furthermore, the SMEF showed inhibition of RANKL-induced ROS production in RAW 264.7 cells. The results suggest that the SMEF, which contained high quantities of RA, could be developed as a natural active pharmaceutical ingredient for osteoclastogenic protection and health promotion.
Keywords: Nga-Mon (Perilla frutescens); RANKL; ROS; anti-inflammation; antioxidant; osteoclastogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

