Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) Plasma Concentration in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Observational Study
- PMID: 33671433
- PMCID: PMC7922575
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11020332
Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) Plasma Concentration in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
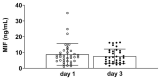
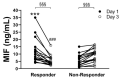
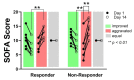
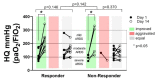
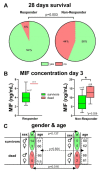
Mortality in critically ill coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients is high and pharmacological treatment strategies remain limited. Early-stage predictive biomarkers are needed to identify patients with a high risk of severe clinical courses and to stratify treatment strategies. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) was previously described as a potential predictor for the outcome of critically ill patients and for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a hallmark of severe COVID-19 disease. This prospective observational study evaluates the predictive potential of MIF for the clinical outcome after severe COVID-19 infection. Plasma MIF concentrations were measured in 36 mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients over three days after intensive care unit (ICU) admission. Increased compared to decreased MIF was significantly associated with aggravated organ function and a significantly lower 28-day survival (sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score; 8.2 ± 4.5 to 14.3 ± 3, p = 0.009 vs. 8.9 ± 1.9 to 12 ± 2, p = 0.296; survival: 56% vs. 93%; p = 0.003). Arterial hypertension was the predominant comorbidity in 85% of patients with increasing MIF concentrations (vs. decreasing MIF: 39%; p = 0.015). Without reaching significance, more patients with decreasing MIF were able to improve their ARDS status (p = 0.142). The identified association between an early MIF response, aggravation of organ function and 28-day survival may open future perspectives for biomarker-based diagnostic approaches for ICU management of COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; Horowitz Quotient; ICU treatment; Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF); SOFA Score; acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mao R., Qiu Y., He J.S., Tan J.Y., Li X.H., Liang J., Shen J., Zhu L.R., Chen Y., Iacucci M., et al. Manifestations and prognosis of gastrointestinal and liver involvement in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020;5:667–678. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30126-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grasselli G., Zangrillo A., Zanella A., Antonelli M., Cabrini L., Castelli A., Cereda D., Coluccello A., Foti G., Fumagalli R., et al. Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. JAMA. 2020;323:1574–1581. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.5394. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

