Compartmentalized Signaling in Aging and Neurodegeneration
- PMID: 33671541
- PMCID: PMC7926881
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10020464
Compartmentalized Signaling in Aging and Neurodegeneration
Abstract
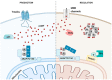
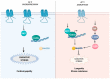
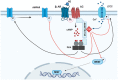
The cyclic AMP (cAMP) signalling cascade is necessary for cell homeostasis and plays important roles in many processes. This is particularly relevant during ageing and age-related diseases, where drastic changes, generally decreases, in cAMP levels have been associated with the progressive decline in overall cell function and, eventually, the loss of cellular integrity. The functional relevance of reduced cAMP is clearly supported by the finding that increases in cAMP levels can reverse some of the effects of ageing. Nevertheless, despite these observations, the molecular mechanisms underlying the dysregulation of cAMP signalling in ageing are not well understood. Compartmentalization is widely accepted as the modality through which cAMP achieves its functional specificity; therefore, it is important to understand whether and how this mechanism is affected during ageing and to define which is its contribution to this process. Several animal models demonstrate the importance of specific cAMP signalling components in ageing, however, how age-related changes in each of these elements affect the compartmentalization of the cAMP pathway is largely unknown. In this review, we explore the connection of single components of the cAMP signalling cascade to ageing and age-related diseases whilst elaborating the literature in the context of cAMP signalling compartmentalization.
Keywords: PKA; aging; cAMP; compartmentalization; neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Burdyga A., Surdo N.C., Monterisi S., Di Benedetto G., Grisan F., Penna E., Pellegrini L., Zaccolo M., Bortolozzi M., Swietach P., et al. Phosphatases control PKA-dependent functional microdomains at the outer mitochondrial membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2018;115:E6497–E6506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1806318115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

