Structure-Based Virtual Screening of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibitors by Cheminformatics Approaches and Bio-Molecular Simulation
- PMID: 33671607
- PMCID: PMC7926523
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11020329
Structure-Based Virtual Screening of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibitors by Cheminformatics Approaches and Bio-Molecular Simulation
Abstract
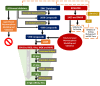
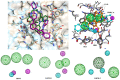
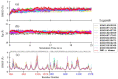
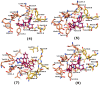
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is a drug target in rheumatoid arthritis and several other auto-immune disorders. TNF-α binds with TNF receptors (TNFR), located on the surface of several immunological cells to exert its effect. Hence, the use of inhibitors that can hinder the complex formation of TNF-α/TNFR can be of medicinal significance. In this study, multiple chem-informatics approaches, including descriptor-based screening, 2D-similarity searching, and pharmacophore modelling were applied to screen new TNF-α inhibitors. Subsequently, multiple-docking protocols were used, and four-fold post-docking results were analyzed by consensus approach. After structure-based virtual screening, seventeen compounds were mutually ranked in top-ranked position by all the docking programs. Those identified hits target TNF-α dimer and effectively block TNF-α/TNFR interface. The predicted pharmacokinetics and physiological properties of the selected hits revealed that, out of seventeen, seven compounds (4, 5, 10, 11, 13-15) possessed excellent ADMET profile. These seven compounds plus three more molecules (7, 8 and 9) were chosen for molecular dynamics simulation studies to probe into ligand-induced structural and dynamic behavior of TNF-α, followed by ligand-TNF-α binding free energy calculation using MM-PBSA. The MM-PBSA calculations revealed that compounds 4, 5, 7 and 9 possess highest affinity for TNF-α; 8, 11, 13-15 exhibited moderate affinities, while compound 10 showed weaker binding affinity with TNF-α. This study provides valuable insights to design more potent and selective inhibitors of TNF-α, that will help to treat inflammatory disorders.
Keywords: 2D-similarity searching; MM-PBSA calculation; absorption; descriptor analysis; distribution; excretion and toxicity (ADMET) prediction; metabolism; molecular docking; molecular dynamics simulation; pharmacophore modelling; tumor necrosis factor–α.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

