Has the Flood Entered the Basement? A Systematic Literature Review about Machine Learning in Laboratory Medicine
- PMID: 33671623
- PMCID: PMC7926482
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11020372
Has the Flood Entered the Basement? A Systematic Literature Review about Machine Learning in Laboratory Medicine
Abstract
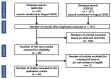
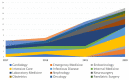
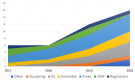
This article presents a systematic literature review that expands and updates a previous review on the application of machine learning to laboratory medicine. We used Scopus and PubMed to collect, select and analyse the papers published from 2017 to the present in order to highlight the main studies that have applied machine learning techniques to haematochemical parameters and to review their diagnostic and prognostic performance. In doing so, we aim to address the question we asked three years ago about the potential of these techniques in laboratory medicine and the need to leverage a tool that was still under-utilised at that time.
Keywords: deep learning; laboratory medicine; laboratory tests; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The Medical Futurist. [(accessed on 1 August 2020)]; Available online: https://medicalfuturist.com/fda-approved-ai-based-algorithms/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources