Properties of the Extracellular Polymeric Substance Layer from Minimally Grown Planktonic Cells of Listeria monocytogenes
- PMID: 33671666
- PMCID: PMC7926710
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11020331
Properties of the Extracellular Polymeric Substance Layer from Minimally Grown Planktonic Cells of Listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
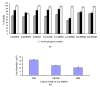
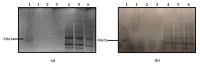
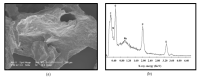
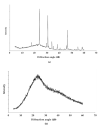
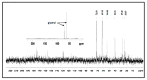
The bacterium Listeria monocytogenes is a serious concern to food processing facilities because of its persistence. When liquid cultures of L. monocytogenes were prepared in defined media, it was noted that planktonic cells rapidly dropped out of suspension. Zeta potential and hydrophobicity assays found that the cells were more negatively charged (-22, -18, -10 mV in defined media D10, MCDB 202 and brain heart infusion [BHI] media, respectively) and were also more hydrophobic. A SEM analysis detected a capsular-like structure on the surface of cells grown in D10 media. A crude extract of the extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) was found to contain cell-associated proteins. The proteins were removed with pronase treatment. The remaining non-proteinaceous component was not stained by Coomassie blue dye and a further chemical analysis of the EPS did not detect significant amounts of sugars, DNA, polyglutamic acid or any other specific amino acid. When the purified EPS was subjected to attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy, the spectra obtained did not match the profile of any of the 12 reference compounds used. An x-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis showed that the EPS was amorphous and a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis detected the presence of glycerol. An elemental energy dispersive x-ray (EDX) analysis showed traces of phosphorous as a major component. In conclusion, it is proposed that the non-proteinaceous component may be phospholipid in nature, possibly derived from the cell wall lipoteichoic acid.
Keywords: L. monocytogenes; bond stretching; capsule; extracellular polymeric substance; minimal media; proteinaceous and non-proteinaceous moiety; spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interaction of Pb(II) and biofilm associated extracellular polymeric substances of a marine bacterium Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes NP103.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2017 Feb 15;173:655-665. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2016.10.009. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2017. PMID: 27788469
-
Infrared spectroscopy with multivariate analysis to interrogate the interaction of whole cells and secreted soluble exopolimeric substances of Pseudomonas veronii 2E with Cd(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II).Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020 Mar 5;228:117820. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.117820. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020. PMID: 31771908
-
Teichoic acid is the major polysaccharide present in the Listeria monocytogenes biofilm matrix.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2016 Jan;363(2):fnv229. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnv229. Epub 2015 Nov 30. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26626878
-
Glycerol metabolism induces Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation at the air-liquid interface.Int J Food Microbiol. 2018 May 20;273:20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.03.009. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Int J Food Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29558680
-
Exopolymeric substances (EPS) from Salmonella enterica: polymers, proteins and their interactions with plants and abiotic surfaces.J Microbiol. 2019 Jan;57(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s12275-019-8353-y. Epub 2018 Sep 6. J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30552630 Review.
Cited by
-
Antilisterial and antioxidant exopolysaccharide from Enterococcus faecium PCH.25 isolated from cow butter: characterization and probiotic potential.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Aug 29;206(9):389. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04112-2. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39210205
-
Mushroom and cereal β-D-glucan solid state NMR and FTIR datasets.Data Brief. 2021 Dec 24;40:107765. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2021.107765. eCollection 2022 Feb. Data Brief. 2021. PMID: 35005151 Free PMC article.
-
Genome and pan-genome analysis of a new exopolysaccharide-producing bacterium Pyschrobacillus sp. isolated from iron ores deposit and insights into iron uptake.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 6;15:1440081. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1440081. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39238887 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genome analysis of the first Listeria monocytogenes core genome multi-locus sequence types CT2050 AND CT2051 strains with their close relatives.AIMS Microbiol. 2022 Mar 21;8(1):61-72. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2022006. eCollection 2022. AIMS Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35496987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomic Approaches to Study the Potential Inhibitory Effects of Plantaricin Q7 against Listeria monocytogenes Biofilm.Foods. 2024 Aug 17;13(16):2573. doi: 10.3390/foods13162573. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39200500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allam M., Tau N., Smouse S.L., Mtshali P.S., Mnyameni F., Khumalo Z.T.H., Ismail A., Govender N., Thomas J., Smith A.M. Whole-Genome sequences of Listeria monocytogenes sequence type 6 isolates associated with a large foodborne outbreak in South Africa, 2017 to 2018. Genome Announc. 2018;6:e00538-18. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00538-18. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

