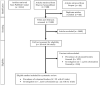
A Systematic Review of Campylobacter jejuni Vaccine Candidates for Chickens
- PMID: 33671947
- PMCID: PMC7919041
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9020397
A Systematic Review of Campylobacter jejuni Vaccine Candidates for Chickens
Abstract
Campylobacter jejuni infection linked to the consumption of contaminated poultry products is one of the leading causes of human enteric illness worldwide. Vaccination of chickens is one of the potential strategies that could be used to control C. jejuni colonization. To date, various C. jejuni vaccines using potential antigens have been evaluated, but a challenge in identifying the most effective formulation is the wide variability in vaccine efficacies reported. A systematic review was undertaken to compare C. jejuni vaccine studies. Based upon specific selection criteria eligible papers were identified and included in the analysis. Vaccine efficacy reported from different C. jejuni antigens, vaccine types, and vaccination regimens reported in these papers were reviewed. Our analysis shows that total outer membrane proteins and cysteine ABC transporter substrate-binding protein were among the most efficacious vaccine antigen candidates reported. This review also highlights the importance of the need for increased consistency in the way C. jejuni vaccine studies in poultry are designed and reported in order to be able to undertake a robust comparison of C. jejuni vaccine candidates.
Keywords: Campylobacter jejuni; chickens; poultry; systematic review; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coadministration of the Campylobacter jejuni N-Glycan-Based Vaccine with Probiotics Improves Vaccine Performance in Broiler Chickens.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Nov 16;83(23):e01523-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01523-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28939610 Free PMC article.
-
In silico prediction and expression analysis of vaccine candidate genes of Campylobacter jejuni.Poult Sci. 2023 May;102(5):102592. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102592. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 36972674 Free PMC article.
-
A DNA prime/protein boost vaccine protocol developed against Campylobacter jejuni for poultry.Vaccine. 2018 Apr 12;36(16):2119-2125. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 29555216
-
Design and data analysis of experimental trials to test vaccine candidates against zoonotic pathogens in animals: the case of a clinical trial against campylobacter in broilers.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012 Oct;11(10):1179-88. doi: 10.1586/erv.12.98. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012. PMID: 23176651 Review.
-
Campylobacter jejuni in Poultry: Pathogenesis and Control Strategies.Microorganisms. 2022 Oct 28;10(11):2134. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10112134. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36363726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Foodborne Pathogen Campylobacter.Microorganisms. 2021 Jun 8;9(6):1241. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061241. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34200984 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Oxford Nanopore Technologies MinION Sequencing Workflow for Campylobacter jejuni Identification in Broilers on Site—A Proof-of-Concept Study.Animals (Basel). 2022 Aug 13;12(16):2065. doi: 10.3390/ani12162065. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009653 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-antigen Campylobacter vaccine enhances antibody responses in layer breeders and sustains elevated maternal antibody levels in their offspring.Poult Sci. 2025 Apr;104(4):104898. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104898. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39985894 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a liposomal subunit vaccine in chickens for reduction of Campylobacter gut colonisation.J Vet Res. 2024 Nov 6;68(4):487-496. doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2024-0062. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39776683 Free PMC article.
-
Intervention Strategies to Control Campylobacter at Different Stages of the Food Chain.Microorganisms. 2023 Jan 1;11(1):113. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010113. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36677405 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- EFSA, Scientific Opinion on Quantification of the risk posed by broiler meat to human campylobacteriosis in the EU. EFSA J. 2010;8:1437. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1437. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases