Immune-Mediated Retinal Vasculitis in Posterior Uveitis and Experimental Models: The Leukotriene (LT)B4-VEGF Axis
- PMID: 33671954
- PMCID: PMC7919050
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10020396
Immune-Mediated Retinal Vasculitis in Posterior Uveitis and Experimental Models: The Leukotriene (LT)B4-VEGF Axis
Abstract
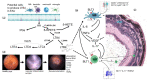
Retinal vascular diseases have distinct, complex and multifactorial pathogeneses yet share several key pathophysiological aspects including inflammation, vascular permeability and neovascularisation. In non-infectious posterior uveitis (NIU), retinal vasculitis involves vessel leakage leading to retinal enlargement, exudation, and macular oedema. Neovascularisation is not a common feature in NIU, however, detection of the major angiogenic factor-vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A)-in intraocular fluids in animal models of uveitis may be an indication for a role for this cytokine in a highly inflammatory condition. Suppression of VEGF-A by directly targeting the leukotriene B4 (LTB4) receptor (BLT1) pathway indicates a connection between leukotrienes (LTs), which have prominent roles in initiating and propagating inflammatory responses, and VEGF-A in retinal inflammatory diseases. Further research is needed to understand how LTs interact with intraocular cytokines in retinal inflammatory diseases to guide the development of novel therapeutic approaches targeting both inflammatory mediator pathways.
Keywords: BLT1; EAU; LTB4; VEGF; inflammation; neovascularisation; retinal vasculitis; uveitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors M.N. and W.W.-D. are employees of Akari Therapeutics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Leukotriene B4 and Its Receptor in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis and in Human Retinal Tissues: Clinical Severity and LTB4 Dependence of Retinal Th17 Cells.Am J Pathol. 2021 Feb;191(2):320-334. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.10.010. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Am J Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33159884
-
Blockade of the interaction of leukotriene b4 with its receptor prevents development of autoimmune uveitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Apr;47(4):1543-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-1238. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 16565390
-
Leukotriene B₄-leukotriene B₄ receptor axis promotes oxazolone-induced contact dermatitis by directing skin homing of neutrophils and CD8⁺ T cells.Immunology. 2015 Sep;146(1):50-8. doi: 10.1111/imm.12478. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 25959240 Free PMC article.
-
LTB4 and BLT1 in inflammatory arthritis.Semin Immunol. 2017 Oct;33:52-57. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2017.09.009. Semin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29042029 Review.
-
Leukotriene B4 receptors as therapeutic targets for ophthalmic diseases.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020 Sep;1865(9):158756. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158756. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020. PMID: 32535236 Review.
Cited by
-
Vascular Signalling.Cells. 2023 Aug 10;12(16):2038. doi: 10.3390/cells12162038. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37626847 Free PMC article.
-
AAV-mediated gene therapies for glaucoma and uveitis: are we there yet?Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024 Apr 15;26:e9. doi: 10.1017/erm.2024.4. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38618935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in Ocular Therapy: A Review of Emerging Drug Delivery Approaches and Pharmaceutical Technologies.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Oct 12;16(10):1325. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101325. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term effects of tocilizumab on retinal and choroidal inflammation in Birdshot uveitis.J Ophthalmic Inflamm Infect. 2024 Nov 21;14(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12348-024-00443-9. J Ophthalmic Inflamm Infect. 2024. PMID: 39570440 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt3a is a promising target in colorectal cancer.Med Oncol. 2023 Jan 31;40(3):86. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-01958-2. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36719558 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

