Nano-Interstice Driven Powerless Blood Plasma Extraction in a Membrane Filter Integrated Microfluidic Device
- PMID: 33671983
- PMCID: PMC7919272
- DOI: 10.3390/s21041366
Nano-Interstice Driven Powerless Blood Plasma Extraction in a Membrane Filter Integrated Microfluidic Device
Abstract
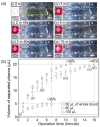
Blood plasma is a source of biomarkers in blood and a simple, fast, and easy extraction method is highly required for point-of-care testing (POCT) applications. This paper proposes a membrane filter integrated microfluidic device to extract blood plasma from whole blood, without any external instrumentation. A commercially available membrane filter was integrated with a newly designed dual-cover microfluidic device to avoid leakage of the extracted plasma and remaining blood cells. Nano-interstices installed on both sides of the microfluidic channels actively draw the extracted plasma from the membrane. The developed device successfully supplied 20 μL of extracted plasma with a high extraction yield (~45%) in 16 min.
Keywords: blood plasma extraction; microfluidics; point-of-care testing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

