Evaluating the Influence of a G-Quadruplex Prone Sequence on the Transactivation Potential by Wild-Type and/or Mutant P53 Family Proteins through a Yeast-Based Functional Assay
- PMID: 33672023
- PMCID: PMC7919268
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12020277
Evaluating the Influence of a G-Quadruplex Prone Sequence on the Transactivation Potential by Wild-Type and/or Mutant P53 Family Proteins through a Yeast-Based Functional Assay
Abstract
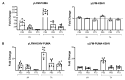
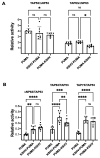
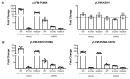
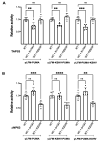
P53, P63, and P73 proteins belong to the P53 family of transcription factors, sharing a common gene organization that, from the P1 and P2 promoters, produces two groups of mRNAs encoding proteins with different N-terminal regions; moreover, alternative splicing events at C-terminus further contribute to the generation of multiple isoforms. P53 family proteins can influence a plethora of cellular pathways mainly through the direct binding to specific DNA sequences known as response elements (REs), and the transactivation of the corresponding target genes. However, the transcriptional activation by P53 family members can be regulated at multiple levels, including the DNA topology at responsive promoters. Here, by using a yeast-based functional assay, we evaluated the influence that a G-quadruplex (G4) prone sequence adjacent to the p53 RE derived from the apoptotic PUMA target gene can exert on the transactivation potential of full-length and N-terminal truncated P53 family α isoforms (wild-type and mutant). Our results show that the presence of a G4 prone sequence upstream or downstream of the P53 RE leads to significant changes in the relative activity of P53 family proteins, emphasizing the potential role of structural DNA features as modifiers of P53 family functions at target promoter sites.
Keywords: G-quadruplex (G4) prone sequence; P53 family; transactivation potential; wild-type and mutant P53/P63 proteins; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The presence of a G-quadruplex prone sequence upstream of a minimal promoter increases transcriptional activity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biosci Rep. 2023 Dec 20;43(12):BSR20231348. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231348. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38112096 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Quadruplex Structure in Proximity to P53 Target Sequences on the Transactivation Potential of P53 Alpha Isoforms.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 24;21(1):127. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010127. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31878115 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical DNA motifs as transactivation targets by wild type and mutant p53.PLoS Genet. 2008 Jun 27;4(6):e1000104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000104. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18714371 Free PMC article.
-
p53/p63/p73 isoforms: an orchestra of isoforms to harmonise cell differentiation and response to stress.Cell Death Differ. 2006 Jun;13(6):962-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401914. Cell Death Differ. 2006. PMID: 16601753 Review.
-
Role of p53 family members in apoptosis.J Cell Physiol. 2000 Feb;182(2):171-81. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(200002)182:2<171::AID-JCP5>3.0.CO;2-3. J Cell Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10623880 Review.
Cited by
-
The presence of a G-quadruplex prone sequence upstream of a minimal promoter increases transcriptional activity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biosci Rep. 2023 Dec 20;43(12):BSR20231348. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231348. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38112096 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Reveals p53 Binding to G-Quadruplex DNA Sequences in Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines.ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2025 Feb 12;5(2):283-298. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.4c00124. eCollection 2025 Apr 16. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2025. PMID: 40255281 Free PMC article.
-
DAXX-ATRX regulation of p53 chromatin binding and DNA damage response.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 26;13(1):5033. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32680-8. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36028493 Free PMC article.
-
A CpG island promoter drives the CXXC5 gene expression.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 2;11(1):15655. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95165-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34341443 Free PMC article.
-
p53/p73 Protein Network in Colorectal Cancer and Other Human Malignancies.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;13(12):2885. doi: 10.3390/cancers13122885. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207603 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaghad M., Bonnet H., Yang A., Creancier L., Biscan J.-C., Valent A., Minty A., Chalon P., Lelias J.-M., Dumont X., et al. Monoallelically expressed gene related to P53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell. 1997;90:809–819. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80540-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang A., Kaghad M., Wang Y., Gillett E., Fleming M.D., Dötsch V., Andrews N.C., Caput D., McKeon F. P63, a P53 homolog at 3q27–29, encodes multiple products with transactivating, death-inducing, and dominant-negative activities. Mol. Cell. 1998;2:305–316. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80275-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

