Sensitivity of the Natriuretic Peptide/cGMP System to Hyperammonaemia in Rat C6 Glioma Cells and GPNT Brain Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 33672024
- PMCID: PMC7919485
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10020398
Sensitivity of the Natriuretic Peptide/cGMP System to Hyperammonaemia in Rat C6 Glioma Cells and GPNT Brain Endothelial Cells
Abstract
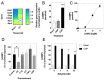
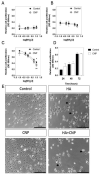
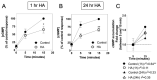
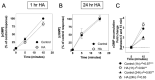
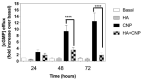
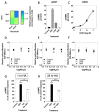
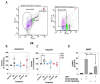
C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) is the major natriuretic peptide of the central nervous system and acts via its selective guanylyl cyclase-B (GC-B) receptor to regulate cGMP production in neurons, astrocytes and endothelial cells. CNP is implicated in the regulation of neurogenesis, axonal bifurcation, as well as learning and memory. Several neurological disorders result in toxic concentrations of ammonia (hyperammonaemia), which can adversely affect astrocyte function. However, the relationship between CNP and hyperammonaemia is poorly understood. Here, we examine the molecular and pharmacological control of CNP in rat C6 glioma cells and rat GPNT brain endothelial cells, under conditions of hyperammonaemia. Concentration-dependent inhibition of C6 glioma cell proliferation by hyperammonaemia was unaffected by CNP co-treatment. Furthermore, hyperammonaemia pre-treatment (for 1 h and 24 h) caused a significant inhibition in subsequent CNP-stimulated cGMP accumulation in both C6 and GPNT cells, whereas nitric-oxide-dependent cGMP accumulation was not affected. CNP-stimulated cGMP efflux from C6 glioma cells was significantly reduced under conditions of hyperammonaemia, potentially via a mechanism involving changed in phosphodiesterase expression. Hyperammonaemia-stimulated ROS production was unaffected by CNP but enhanced by a nitric oxide donor in C6 cells. Extracellular vesicle production from C6 cells was enhanced by hyperammonaemia, and these vesicles caused impaired CNP-stimulated cGMP signalling in GPNT cells. Collectively, these data demonstrate functional interaction between CNP signalling and hyperammonaemia in C6 glioma and GPNT cells, but the exact mechanisms remain to be established.
Keywords: astrocyte; cGMP; endothelial cells; extracellular vesicles; hyperammonaemia; natriuretic peptides; neuroendocrinology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
C-type natriuretic peptide regulation of guanosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate production in human endothelial cells.Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2010 Jul;30(3):185-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.2009.00449.x. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20085572
-
C-type natriuretic peptide-induced relaxation through cGMP-dependent protein kinase and SERCA activation is impaired in two kidney-one clip rat aorta.Life Sci. 2021 May 1;272:119223. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119223. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33610574
-
Ammonia inhibits the C-type natriuretic peptide-dependent cyclic GMP synthesis and calcium accumulation in a rat brain endothelial cell line.Neurochem Int. 2008 May;52(6):1160-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2007.12.005. Epub 2007 Dec 15. Neurochem Int. 2008. PMID: 18222015
-
Molecular Analysis of Sensory Axon Branching Unraveled a cGMP-Dependent Signaling Cascade.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 24;19(5):1266. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051266. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29695045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic GMP pathways in hepatic encephalopathy. Neurological and therapeutic implications.Metab Brain Dis. 2010 Mar;25(1):39-48. doi: 10.1007/s11011-010-9184-z. Epub 2010 Mar 2. Metab Brain Dis. 2010. PMID: 20195723 Review.
Cited by
-
Retinal degeneration protein 3 controls membrane guanylate cyclase activities in brain tissue.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Dec 21;15:1076430. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1076430. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36618828 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK Modulates the Metabolic Adaptation of C6 Glioma Cells in Glucose-Deprived Conditions without Affecting Glutamate Transport.Cells. 2022 May 31;11(11):1800. doi: 10.3390/cells11111800. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681495 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and Genetic Disruption of C-Type Natriuretic Peptide (nppcl) Expression in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Causes Stunted Growth during Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 18;24(16):12921. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612921. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629102 Free PMC article.
-
Facilitating drug delivery in the central nervous system by opening the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier with a single low energy shockwave pulse.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022 Jan 6;19(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12987-021-00303-x. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022. PMID: 34991647 Free PMC article.
-
C-Type Natriuretic Peptide (CNP) Could Improve Sperm Motility and Reproductive Function of Asthenozoospermia.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 8;23(18):10370. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810370. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142279 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

