Interventions Facilitating Family Communication of Genetic Testing Results and Cascade Screening in Hereditary Breast/Ovarian Cancer or Lynch Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33672149
- PMCID: PMC7926393
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13040925
Interventions Facilitating Family Communication of Genetic Testing Results and Cascade Screening in Hereditary Breast/Ovarian Cancer or Lynch Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
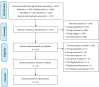
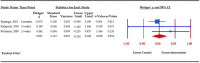
Evidence-based guidelines recommend cascade genetic testing of blood relatives of known Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) or Lynch Syndrome (LS) cases, to inform individualized cancer screening and prevention plans. The study identified interventions designed to facilitate family communication of genetic testing results and/or cancer predisposition cascade genetic testing for HBOC and LS. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials that assessed intervention efficacy for these two outcomes. Additional outcomes were also recorded and synthesized when possible. Fourteen articles met the inclusion criteria and were included in the narrative synthesis and 13 in the meta-analysis. Lack of participant blinding was the most common risk of bias. Interventions targeted HBOC (n = 5); both HBOC and LS (n = 4); LS (n = 3); or ovarian cancer (n = 2). All protocols (n = 14) included a psychoeducational and/or counseling component. Additional components were decision aids (n = 4), building communication skills (n = 4), or motivational interviewing (n = 1). The overall effect size for family communication was small (g = 0.085) and not significant (p = 0.344), while for cascade testing, it was small (g = 0.169) but significant (p = 0.014). Interventions show promise for improving cancer predisposition cascade genetic testing for HBOC and LS. Future studies should employ family-based approaches and include racially diverse samples.
Keywords: Tier-1 genetic conditions; intervention efficacy; psychoeducational interventions; randomized controlled trials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Allemani C., Weir H.K., Carreira H., Harewood R., Spika D., Wang X.S., Bannon F., Ahn J.V., Johnson C.J., Bonaventure A., et al. Global surveillance of cancer survival 1995–2009: Analysis of individual data for 25,676,887 patients from 279 population-based registries in 67 countries (Concord-2) Lancet. 2015;385:977–1010. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62038-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chubb D., Broderick P., Frampton M., Kinnersley B., Sherborne A., Penegar S., Lloyd A., Ma Y.P., Dobbins S.E., Houlston R.S. Genetic diagnosis of high-penetrance susceptibility for colorectal cancer (CRC) is achievable for a high proportion of familial CRC by exome sequencing. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015;33:426–432. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.56.5689. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Walsh T., Casadei S., Lee M.K., Pennil C.C., Nord A.S., Thornton A.M., Roeb W., Agnew K.J., Stray S.M., Wickramanayake A., et al. Mutations in 12 genes for inherited ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal carcinoma identified by massively parallel sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:18032–18037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115052108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous