Overexpression of miR-1306-5p, miR-3195, and miR-3914 Inhibits Ameloblast Differentiation through Suppression of Genes Associated with Human Amelogenesis Imperfecta
- PMID: 33672174
- PMCID: PMC7926528
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22042202
Overexpression of miR-1306-5p, miR-3195, and miR-3914 Inhibits Ameloblast Differentiation through Suppression of Genes Associated with Human Amelogenesis Imperfecta
Abstract
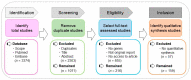
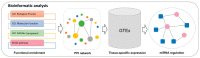
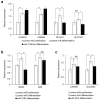
Amelogenesis imperfecta is a congenital form of enamel hypoplasia. Although a number of genetic mutations have been reported in humans, the regulatory network of these genes remains mostly unclear. To identify signatures of biological pathways in amelogenesis imperfecta, we conducted bioinformatic analyses on genes associated with the condition in humans. Through an extensive search of the main biomedical databases, we found 56 genes in which mutations and/or association/linkage were reported in individuals with amelogenesis imperfecta. These candidate genes were further grouped by function, pathway, protein-protein interaction, and tissue-specific expression patterns using various bioinformatic tools. The bioinformatic analyses highlighted a group of genes essential for extracellular matrix formation. Furthermore, advanced bioinformatic analyses for microRNAs (miRNAs), which are short non-coding RNAs that suppress target genes at the post-transcriptional level, predicted 37 candidates that may be involved in amelogenesis imperfecta. To validate the miRNA-gene regulation association, we analyzed the target gene expression of the top seven candidate miRNAs: miR-3195, miR-382-5p, miR-1306-5p, miR-4683, miR-6716-3p, miR-3914, and miR-3935. Among them, miR-1306-5p, miR-3195, and miR-3914 were confirmed to regulate ameloblast differentiation through the regulation of genes associated with amelogenesis imperfecta in AM-1 cells, a human ameloblastoma cell line. Taken together, our study suggests a potential role for miRNAs in amelogenesis imperfecta.
Keywords: amelogenesis imperfecta; enamel formation; microRNAs; tooth development; tooth formation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Crucial Roles of microRNA-16-5p and microRNA-27b-3p in Ameloblast Differentiation Through Regulation of Genes Associated With Amelogenesis Imperfecta.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 25;13:788259. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.788259. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35401675 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy Plays a Crucial Role in Ameloblast Differentiation.J Dent Res. 2023 Aug;102(9):1047-1057. doi: 10.1177/00220345231169220. Epub 2023 May 30. J Dent Res. 2023. PMID: 37249312 Free PMC article.
-
Crucial Role of microRNAs as New Targets for Amelogenesis Disorders Detection.Curr Drug Targets. 2023;24(14):1139-1149. doi: 10.2174/0113894501257011231030161427. Curr Drug Targets. 2023. PMID: 37936447
-
Enamel matrix proteins and ameloblast biology.Connect Tissue Res. 1995;32(1-4):97-107. doi: 10.3109/03008209509013710. Connect Tissue Res. 1995. PMID: 7554940 Review.
-
[Alteración del gen AMELX en amelogénesis imperfecta. Una breve revisión].Gac Med Mex. 2019;155(1):101-107. doi: 10.24875/GMM.18003604. Gac Med Mex. 2019. PMID: 30799455 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Crucial Roles of microRNA-16-5p and microRNA-27b-3p in Ameloblast Differentiation Through Regulation of Genes Associated With Amelogenesis Imperfecta.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 25;13:788259. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.788259. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35401675 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying a novel IRF3/circUHRF1/miR-1306-5p/ARL4C axis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression.Cell Cycle. 2022 Feb;21(4):392-405. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.2020450. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Cell Cycle. 2022. PMID: 34983293 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-1306-5p Regulates the METTL14-Guided m6A Methylation to Repress Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Sep 7;2022:5787808. doi: 10.1155/2022/5787808. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9831697. doi: 10.1155/2023/9831697. PMID: 36118827 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Ugonin inhibits chondrosarcoma metastasis through suppressing cathepsin V via promoting miR-4799-5p expression.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jan 13;21(3):1144-1157. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.106827. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39897041 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNAs and tooth development: The role of microRNAs in tooth agenesis and impaction.J Dent Sci. 2024 Oct;19(4):2150-2156. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2024.03.013. Epub 2024 Mar 22. J Dent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39347023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balic A., Thesleff I. Tissue Interactions Regulating Tooth Development and Renewal. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015;115:157–186. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

