Expeller-Pressed Canola (Brassica napus) Meal Modulates the Structure and Function of the Cecal Microbiota, and Alters the Metabolome of the Pancreas, Liver, and Breast Muscle of Broiler Chickens
- PMID: 33672178
- PMCID: PMC7926547
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11020577
Expeller-Pressed Canola (Brassica napus) Meal Modulates the Structure and Function of the Cecal Microbiota, and Alters the Metabolome of the Pancreas, Liver, and Breast Muscle of Broiler Chickens
Abstract
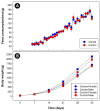
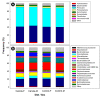
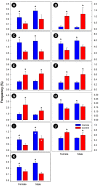
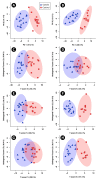
The inoculation of one-day-old broiler chicks with the cecal contents from a mature broiler breeder resulted in a highly diverse and uniform cecal bacterial community. CM did not affect feed consumption, weight gain, nor the richness, evenness, or diversity of the cecal bacterial community. However, the structure of the bacterial community was altered in birds fed the CM diet. Although the CM diet was formulated to contain equivalent metabolizable energy to the control diet, it contained more dietary fiber. The abundance of bacterial families, including those that are known to contain species able to metabolize fiber was altered (e.g., bacteria within the families, Methanobacteriaceae, Atopobiaceae, Prevotellaceae, Clostridiales Family XIII, Peptostreptococcaceae, and Succinivibrionaceae), and concentrations of SCFAs were higher in the ceca of birds fed the CM diet. Moreover, concentrations of isoleucine, isobutyrate, glutamate, and 2-oxoglutarate were higher, whereas concentrations of phenyllactic acid, indole, glucose, 3-phenylpropionate, and 2-oxobutyrate were lower in the digesta of chickens that were fed CM. The metabolic profiles of pancreas, liver, and breast muscle tissues of birds fed the CM diet differed from control birds. Metabolites that were associated with energy production, protection against oxidative stress, and pathways of amino acid and glycerophospholipid metabolism had altered concentrations in these tissues. Some of the observed changes in metabolite levels may indicate an increased disease risk in birds fed the CM diet (e.g., pancreatitis), and others suggested that birds mounted metabolic response to offset the adverse impacts of CM (e.g., oxidative stress in the liver).
Keywords: breast muscle; broiler chickens; canola meal; cecum; liver; metabolome; microbiota; pancreas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Government of Canada . Statistics Canada; 2020. [(accessed on 17 February 2021)]. Canola: A Canadian Success Story. Available online: https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/96-325-x/2007000/article/10778-eng.htm.
-
- Canola Council of Canada . Canola Council of Canada; 2015. [(accessed on 17 February 2021)]. Canola Meal Feeding Guide. Available online: https://www.canolacouncil.org/download/215/pages/5344/2015_canola_meal_f....
-
- Pratt S. New Canola Could Open Up Feed Market. Western Producer. [(accessed on 17 February 2021)];2016 Available online: https://www.producer.com/news/new-canola-could-open-up-feed-market/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

