Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Na+/H+ Exchangers tNhe3a and tNhe3b Display Unique Inhibitory Profiles Dissimilar from Mammalian NHE Isoforms
- PMID: 33672216
- PMCID: PMC7926675
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22042205
Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Na+/H+ Exchangers tNhe3a and tNhe3b Display Unique Inhibitory Profiles Dissimilar from Mammalian NHE Isoforms
Abstract
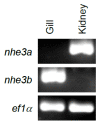
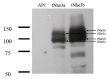
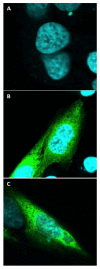
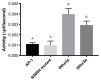
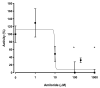
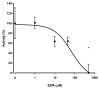
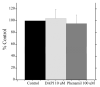
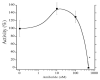
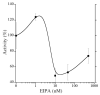
Freshwater fishes maintain an internal osmolality of ~300 mOsm, while living in dilute environments ranging from 0 to 50 mOsm. This osmotic challenge is met at least partially, by Na+/H+ exchangers (NHE) of fish gill and kidney. In this study, we cloned, expressed, and pharmacologically characterized fish-specific Nhes of the commercially important species Oncorhynchus mykiss. Trout (t) Nhe3a and Nhe3b isoforms from gill and kidney were expressed and characterized in an NHE-deficient cell line. Western blotting and immunocytochemistry confirmed stable expression of the tagged trout tNhe proteins. To measure NHE activity, a transient acid load was induced in trout tNhe expressing cells and intracellular pH was measured. Both isoforms demonstrated significant activity and recovered from an acute acid load. The effect of the NHE transport inhibitors amiloride, EIPA (5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl)-amiloride), phenamil, and DAPI was examined. tNhe3a was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by amiloride and EIPA and tNhe3a was more sensitive to amiloride than EIPA, unlike mammalian NHE1. tNhe3b was inhibited by high concentrations of amiloride, while even in the presence of high concentrations of EIPA (500 µM), some activity of tNhe3b remained. Phenamil and DAPI were ineffective at inhibiting tNhe activity of either isoform. The current study aids in understanding the pharmacology of fish ion transporters. Both isoforms display inhibitory profiles uniquely different from mammalian NHEs and show resistance to inhibition. Our study allows for more direct interpretation of past, present, and future fish-specific sodium transport studies, with less reliance on mammalian NHE data for interpretation.
Keywords: AP-1; fish physiology; ion-regulation; pH regulation; pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potency and specificity of amiloride and its analogues on branchial sodium fluxes in freshwater trout and goldfish.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2024 Nov;297:111715. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2024.111715. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39089444
-
Characterization of developmental Na(+) uptake in rainbow trout larvae supports a significant role for Nhe3b.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2016 Nov;201:30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.06.027. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27350321
-
Ammonia transport across the skin of adult rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to high environmental ammonia (HEA).J Comp Physiol B. 2014 Jan;184(1):77-90. doi: 10.1007/s00360-013-0784-x. Epub 2013 Oct 11. J Comp Physiol B. 2014. PMID: 24114656
-
Hormonal regulation, pharmacology, and membrane sorting of vertebrate Na+/H+ exchanger isoforms.Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 1):C283-96. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.2.C283. Am J Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7864067 Review.
-
Sodium-dependent copper uptake across epithelia: a review of rationale with experimental evidence from gill and intestine.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Nov 13;1566(1-2):104-15. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(02)00590-4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12421542 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification of the NHE gene family in Coilia nasus and its response to salinity challenge and ammonia stress.BMC Genomics. 2022 Jul 20;23(1):526. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08761-9. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35858854 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

