Therapeutic Targeting of MicroRNAs in the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 33672261
- PMCID: PMC7926641
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22042210
Therapeutic Targeting of MicroRNAs in the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
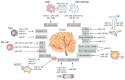
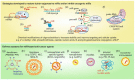
The tumor-microenvironment (TME) is an amalgamation of various factors derived from malignant cells and infiltrating host cells, including cells of the immune system. One of the important factors of the TME is microRNAs (miRs) that regulate target gene expression at a post transcriptional level. MiRs have been found to be dysregulated in tumor as well as in stromal cells and they emerged as important regulators of tumorigenesis. In fact, miRs regulate almost all hallmarks of cancer, thus making them attractive tools and targets for novel anti-tumoral treatment strategies. Tumor to stroma cell cross-propagation of miRs to regulate protumoral functions has been a salient feature of the TME. MiRs can either act as tumor suppressors or oncogenes (oncomiRs) and both miR mimics as well as miR inhibitors (antimiRs) have been used in preclinical trials to alter cancer and stromal cell phenotypes. Owing to their cascading ability to regulate upstream target genes and their chemical nature, which allows specific pharmacological targeting, miRs are attractive targets for anti-tumor therapy. In this review, we cover a recent update on our understanding of dysregulated miRs in the TME and provide an overview of how these miRs are involved in current cancer-therapeutic approaches from bench to bedside.
Keywords: RNA therapy; breast cancer; inflammation; macrophage; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the literature; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-A Tumor Trojan Horse for Tumor-Associated Macrophages.Cells. 2019 Nov 21;8(12):1482. doi: 10.3390/cells8121482. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31766495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal and Non-Exosomal MicroRNAs: New Kids on the Block for Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 19;23(9):4493. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094493. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35562884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs and gene regulation in breast cancer.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020 Nov;34(11):e22567. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22567. Epub 2020 Jul 30. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32729651 Review.
-
The emerging roles of exosomes in anti-cancer drug resistance and tumor progression: An insight towards tumor-microenvironment interaction.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Jan;1875(1):188488. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188488. Epub 2020 Nov 30. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33271308 Review.
-
Role of microRNAs in remodeling the tumor microenvironment (Review).Int J Oncol. 2020 Feb;56(2):407-416. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4952. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Int J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31894326 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amplifying gene expression with RNA-targeted therapeutics.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023 Jul;22(7):539-561. doi: 10.1038/s41573-023-00704-7. Epub 2023 May 30. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023. PMID: 37253858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome: an overview on enhanced biogenesis by small molecules.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;398(6):6473-6508. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03762-9. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39862264 Review.
-
Delivery of miRNAs Using Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Osteosarcoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Aug 22;19:8641-8660. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S471900. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39188861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trials and Tribulations of MicroRNA Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 25;25(3):1469. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031469. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Gnrhr: A Checkpoint for Metabolic Control of Female Reproduction.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 24;22(7):3312. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073312. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33805020 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

