Analysis of Body Perception, Preworkout Meal Habits and Bone Resorption in Child Gymnasts
- PMID: 33672264
- PMCID: PMC7926894
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18042184
Analysis of Body Perception, Preworkout Meal Habits and Bone Resorption in Child Gymnasts
Abstract
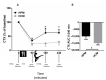
The beneficial effects of physical activity on body image perception and bone are debated among artistic gymnasts. Gymnasts seem to be at greater risk of developing body dissatisfaction, eating disorders and osteoporosis due to inadequate nutrition and attention to the appearance of the body. The objective of this work was to investigate the association between the artistic gymnast and a more favorable body image compared to their sedentary peers and if a preworkout high-carbohydrate meal (HCM; 300 kcal, 88% carbohydrates, 9% protein, 3% fat) or high-protein meal (HPM; 300 kcal, 55% carbohydrates, 31% protein, 13% fat) is able to attenuate bone resorption in young rhythmic gymnasts. Twenty-eight preadolescent female gymnasts were examined. Self-esteem tests were used to analyze body image perception. Preworkout eating habits were examined by short food frequency questions (FFQ) validated for children. The biomarker of the bone resorption C-terminal telopeptide region of collagen type 1 (CTX) was measured in the urine (fasting, postmeal and postworkout). Gymnasts reported higher satisfaction with their body appearance compared to sedentary peers. Of the gymnasts, 30% did not have a preworkout meal regularly, and the timing of the consumption was variable. Bone resorption was decreased by the HCM, consumed 90 min before the training, with respect to the HPM. The study suggests that playing artistic gymnastics is associated with a positive body self-perception in a child. The variability in preworkout meal frequency and timing need attention to prevent inadequate eating habits in light of the ability of the HCM to reduce acute bone resorption.
Keywords: aesthetic sports; body image perception; bone resorption; children; physical activity; pre-workout eating habits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

