A 10-Year Probability Deep Neural Network Prediction Model for Lung Cancer
- PMID: 33672275
- PMCID: PMC7926302
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13040928
A 10-Year Probability Deep Neural Network Prediction Model for Lung Cancer
Abstract
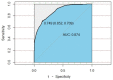
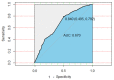
Cancer is the leading cause of death in Taiwan. According to the Cancer Registration Report of Taiwan's Ministry of Health and Welfare, a total of 13,488 people suffered from lung cancer in 2016, making it the second-most common cancer and the leading cancer in men. Compared with other types of cancer, the incidence of lung cancer is high. In this study, the National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRDB) was used to determine the diseases and symptoms associated with lung cancer, and a 10-year probability deep neural network prediction model for lung cancer was developed. The proposed model could allow patients with a high risk of lung cancer to receive an earlier diagnosis and support the physicians' clinical decision-making. The study was designed as a cohort study. The subjects were patients who were diagnosed with lung cancer between 2000 and 2009, and the patients' disease histories were back-tracked for a period, extending to ten years before the diagnosis of lung cancer. As a result, a total of 13 diseases were selected as the predicting factors. A nine layers deep neural network model was created to predict the probability of lung cancer, depending on the different pre-diagnosed diseases, and to benefit the earlier detection of lung cancer in potential patients. The model is trained 1000 times, the batch size is set to 100, the SGD (Stochastic gradient descent) optimizer is used, the learning rate is set to 0.1, and the momentum is set to 0.1. The proposed model showed an accuracy of 85.4%, a sensitivity of 72.4% and a specificity of 85%, as well as an 87.4% area under ROC (AUROC) (95%, 0.8604-0.8885) model precision. Based on data analysis and deep learning, our prediction model discovered some features that had not been previously identified by clinical knowledge. This study tracks a decade of clinical diagnostic records to identify possible symptoms and comorbidities of lung cancer, allows early prediction of the disease, and assists more patients with early diagnosis.
Keywords: deep neural network model; early diagnosis; health prevention; lung cancer; machine learning; prediction model.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Karihtala P., Puistola U. Cancer in an elderly woman. Duodecim Laaketieteellinen Aikakauskirja. 2015;131:1507–1512. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials