A Systematic Review of PET Textural Analysis and Radiomics in Cancer
- PMID: 33672285
- PMCID: PMC7926413
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11020380
A Systematic Review of PET Textural Analysis and Radiomics in Cancer
Abstract
Background: Although many works have supported the utility of PET radiomics, several authors have raised concerns over the robustness and replicability of the results. This study aimed to perform a systematic review on the topic of PET radiomics and the used methodologies.
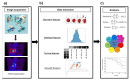
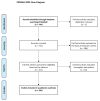
Methods: PubMed was searched up to 15 October 2020. Original research articles based on human data specifying at least one tumor type and PET image were included, excluding those that apply only first-order statistics and those including fewer than 20 patients. Each publication, cancer type, objective and several methodological parameters (number of patients and features, validation approach, among other things) were extracted.
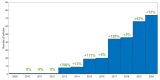
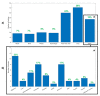
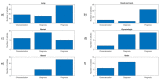
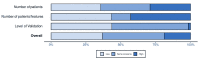
Results: A total of 290 studies were included. Lung (28%) and head and neck (24%) were the most studied cancers. The most common objective was prognosis/treatment response (46%), followed by diagnosis/staging (21%), tumor characterization (18%) and technical evaluations (15%). The average number of patients included was 114 (median = 71; range 20-1419), and the average number of high-order features calculated per study was 31 (median = 26, range 1-286).
Conclusions: PET radiomics is a promising field, but the number of patients in most publications is insufficient, and very few papers perform in-depth validations. The role of standardization initiatives will be crucial in the upcoming years.
Keywords: PET; cancer; heterogeneity; radiomics; textural analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiomics in Oncological PET Imaging: A Systematic Review-Part 1, Supradiaphragmatic Cancers.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 May 27;12(6):1329. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12061329. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CT radiomics and PET radiomics: ready for clinical implementation?Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Dec;63(4):355-370. doi: 10.23736/S1824-4785.19.03192-3. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31527578 Review.
-
18F-FDG PET radiomics approaches: comparing and clustering features in cervical cancer.Ann Nucl Med. 2017 Nov;31(9):678-685. doi: 10.1007/s12149-017-1199-7. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Ann Nucl Med. 2017. PMID: 28815452
-
Evaluation of the Prognostic Value of FDG PET/CT Parameters for Patients With Surgically Treated Head and Neck Cancer: A Systematic Review.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 May 1;146(5):471-479. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2020.0014. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 32215611
-
On the impact of smoothing and noise on robustness of CT and CBCT radiomics features for patients with head and neck cancers.Med Phys. 2017 May;44(5):1755-1770. doi: 10.1002/mp.12188. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28261818
Cited by
-
Coefficient of variation and texture analysis of 18F-FDG PET/CT images for the prediction of outcome in patients with multiple myeloma.Ann Hematol. 2024 Sep;103(9):3713-3721. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05905-7. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39046513 Free PMC article.
-
Four-dimensional quantitative analysis using FDG-PET in clinical oncology.Jpn J Radiol. 2023 Aug;41(8):831-842. doi: 10.1007/s11604-023-01411-4. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Jpn J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36947283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiomics in Oncological PET Imaging: A Systematic Review-Part 2, Infradiaphragmatic Cancers, Blood Malignancies, Melanoma and Musculoskeletal Cancers.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 May 27;12(6):1330. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12061330. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Joint EANM/SNMMI guideline on radiomics in nuclear medicine : Jointly supported by the EANM Physics Committee and the SNMMI Physics, Instrumentation and Data Sciences Council.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023 Jan;50(2):352-375. doi: 10.1007/s00259-022-06001-6. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36326868 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic 18F-FDG Radiomic Features in Advanced High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Nov 7;13(22):3394. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13223394. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gerlinger M., Rowan A.J., Horswell S., Larkin J., Endesfelder D., Gronroos E., Martinez P., Matthews N., Stewart A., Tarpey P., et al. Intratumor Heterogeneity and Branched Evolution Revealed by Multiregion Sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;366:883–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1113205. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

