KRAB-ZFP Transcriptional Regulators Acting as Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors: An Overview
- PMID: 33672287
- PMCID: PMC7926519
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22042212
KRAB-ZFP Transcriptional Regulators Acting as Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors: An Overview
Abstract
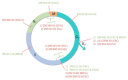
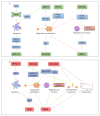
Krüppel-associated box zinc finger proteins (KRAB-ZFPs) constitute the largest family of transcriptional factors exerting co-repressor functions in mammalian cells. In general, KRAB-ZFPs have a dual structure. They may bind to specific DNA sequences via zinc finger motifs and recruit a repressive complex through the KRAB domain. Such a complex mediates histone deacetylation, trimethylation of histone 3 at lysine 9 (H3K9me3), and subsequent heterochromatization. Nevertheless, apart from their repressive role, KRAB-ZFPs may also co-activate gene transcription, likely through interaction with other factors implicated in transcriptional control. KRAB-ZFPs play essential roles in various biological processes, including development, imprinting, retroelement silencing, and carcinogenesis. Cancer cells possess multiple genomic, epigenomic, and transcriptomic aberrations. A growing number of data indicates that the expression of many KRAB-ZFPs is altered in several tumor types, in which they may act as oncogenes or tumor suppressors. Hereby, we review the available literature describing the oncogenic and suppressive roles of various KRAB-ZFPs in cancer. We focused on their association with the clinicopathological features and treatment response, as well as their influence on the cancer cell phenotype. Moreover, we summarized the identified upstream and downstream molecular mechanisms that may govern the functioning of KRAB-ZFPs in a cancer setting.
Keywords: KRAB-ZFPs; ZBRK1; ZFP57; ZKSCAN3; ZNF224; ZNF300; ZNF471; cancer; epigenetic repressor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

