Worms, Fat, and Death: Caenorhabditis elegans Lipid Metabolites Regulate Cell Death
- PMID: 33672292
- PMCID: PMC7926963
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo11020125
Worms, Fat, and Death: Caenorhabditis elegans Lipid Metabolites Regulate Cell Death
Abstract
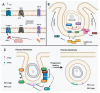
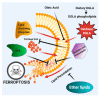
Caenorhabditis elegans is well-known as the model organism used to elucidate the genetic pathways underlying the first described form of regulated cell death, apoptosis. Since then, C. elegans investigations have contributed to the further understanding of lipids in apoptosis, especially the roles of phosphatidylserines and phosphatidylinositols. More recently, studies in C. elegans have shown that dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids can induce the non-apoptotic, iron-dependent form of cell death, ferroptosis. In this review, we examine the roles of various lipids in specific aspects of regulated cell death, emphasizing recent work in C. elegans.
Keywords: apoptosis; ferroptosis; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

