Cell-to-Cell Communication by Host-Released Extracellular Vesicles in the Gut: Implications in Health and Disease
- PMID: 33672304
- PMCID: PMC7927122
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22042213
Cell-to-Cell Communication by Host-Released Extracellular Vesicles in the Gut: Implications in Health and Disease
Abstract
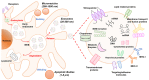
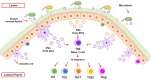
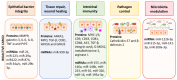
Communication between cells is crucial to preserve body homeostasis and health. Tightly controlled intercellular dialog is particularly relevant in the gut, where cells of the intestinal mucosa are constantly exposed to millions of microbes that have great impact on intestinal homeostasis by controlling barrier and immune functions. Recent knowledge involves extracellular vesicles (EVs) as mediators of such communication by transferring messenger bioactive molecules including proteins, lipids, and miRNAs between cells and tissues. The specific functions of EVs principally depend on the internal cargo, which upon delivery to target cells trigger signal events that modulate cellular functions. The vesicular cargo is greatly influenced by genetic, pathological, and environmental factors. This finding provides the basis for investigating potential clinical applications of EVs as therapeutic targets or diagnostic biomarkers. Here, we review current knowledge on the biogenesis and cargo composition of EVs in general terms. We then focus the attention to EVs released by cells of the intestinal mucosa and their impact on intestinal homeostasis in health and disease. We specifically highlight their role on epithelial barrier integrity, wound healing of epithelial cells, immunity, and microbiota shaping. Microbiota-derived EVs are not reviewed here.
Keywords: exosomes; extracellular vesicles; gut communication; gut immunity; intestinal homeostasis; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Théry C., Witwer K.W., Aikawa E., Alcaraz M.J., Anderson J.D., Andriantsitohaina R., Antoniou A., Arab T., Archer F., Atkin-Smith G.K., et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2018;7:1–42. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang H., Freitas D., Kim H.S., Fabijanic K., Li Z., Chen H., Mark M.T., Molina H., Martin A.B., Bojmar L., et al. Identification of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric-flow field-flow fractionation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018;20:332–343. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0040-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

