Establishing an Analogue Based In Silico Pipeline in the Pursuit of Novel Inhibitory Scaffolds against the SARS Coronavirus 2 Papain-Like Protease
- PMID: 33672721
- PMCID: PMC7924369
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26041134
Establishing an Analogue Based In Silico Pipeline in the Pursuit of Novel Inhibitory Scaffolds against the SARS Coronavirus 2 Papain-Like Protease
Abstract
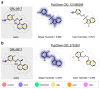
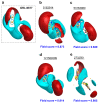
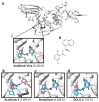
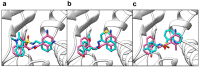
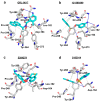
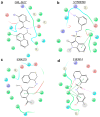
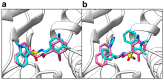
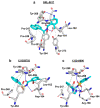
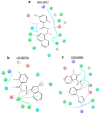
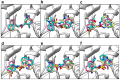
The ongoing coronavirus pandemic has been a burden on the worldwide population, with mass fatalities and devastating socioeconomic consequences. It has particularly drawn attention to the lack of approved small-molecule drugs to inhibit SARS coronaviruses. Importantly, lessons learned from the SARS outbreak of 2002-2004, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1), can be applied to current drug discovery ventures. SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 both possess two cysteine proteases, the main protease (Mpro) and the papain-like protease (PLpro), which play a significant role in facilitating viral replication, and are important drug targets. The non-covalent inhibitor, GRL-0617, which was found to inhibit replication of SARS-CoV-1, and more recently SARS-CoV-2, is the only PLpro inhibitor co-crystallised with the recently solved SARS-CoV-2 PLpro crystal structure. Therefore, the GRL-0617 structural template and pharmacophore features are instrumental in the design and development of more potent PLpro inhibitors. In this work, we conducted scaffold hopping using GRL-0617 as a reference to screen over 339,000 ligands in the chemical space using the ChemDiv, MayBridge, and Enamine screening libraries. Twenty-four distinct scaffolds with structural and electrostatic similarity to GRL-0617 were obtained. These proceeded to molecular docking against PLpro using the AutoDock tools. Of two compounds that showed the most favourable predicted binding affinities to the target site, as well as comparable protein-ligand interactions to GRL-0617, one was chosen for further analogue-based work. Twenty-seven analogues of this compound were further docked against the PLpro, which resulted in two additional hits with promising docking profiles. Our in silico pipeline consisted of an integrative four-step approach: (1) ligand-based virtual screening (scaffold-hopping), (2) molecular docking, (3) an analogue search, and, (4) evaluation of scaffold drug-likeness, to identify promising scaffolds and eliminate those with undesirable properties. Overall, we present four novel, and lipophilic, scaffolds obtained from an exhaustive search of diverse and uncharted regions of chemical space, which may be further explored in vitro through structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies in the search for more potent inhibitors. Furthermore, these scaffolds were predicted to have fewer off-target interactions than GRL-0617. Lastly, to our knowledge, this work contains the largest ligand-based virtual screen performed against GRL-0617.
Keywords: COVID-19; PLpro; SARS coronavirus 2; analogues; docking; drug discovery; in silico; papain-like protease; scaffold hopping; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Naphthalen-1-ylethanamine-containing small molecule inhibitors of the papain-like protease of SARS-CoV-2.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Dec 15;280:116963. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116963. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39442336
-
Interaction of small molecules with the SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease: In silico studies and in vitro validation of protease activity inhibition using an enzymatic inhibition assay.J Mol Graph Model. 2021 May;104:107851. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2021.107851. Epub 2021 Jan 26. J Mol Graph Model. 2021. PMID: 33556646 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease inhibitors through machine learning and molecular simulation approaches.Drug Discov Ther. 2025 Jul 4;19(3):189-199. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2025.01034. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Drug Discov Ther. 2025. PMID: 40571587
-
Design of inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease deriving from GRL0617: Structure-activity relationships.Bioorg Med Chem. 2024 Nov 1;113:117909. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.117909. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Bioorg Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39288705 Review.
-
An Updated Review on SARS-CoV-2 Main Proteinase (MPro): Protein Structure and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21(6):442-460. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666201207095117. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33292134 Review.
Cited by
-
Main and papain-like proteases as prospective targets for pharmacological treatment of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.RSC Adv. 2023 Dec 6;13(50):35500-35524. doi: 10.1039/d3ra06479d. eCollection 2023 Nov 30. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 38077980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico screening of phenylethanoid glycosides, a class of pharmacologically active compounds as natural inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 proteases.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023;21:1461-1472. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.02.020. Epub 2023 Feb 11. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 36817956 Free PMC article.
-
Human soluble CD39 displays substrate inhibition in a substrate-specific manner.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 2;13(1):8958. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36257-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37268726 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphenolic Compounds Isolated from Marine Algae Attenuate the Replication of SARS-CoV-2 in the Host Cell through a Multi-Target Approach of 3CLpro and PLpro.Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 19;20(12):786. doi: 10.3390/md20120786. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36547933 Free PMC article.
-
9-aminominocycline potentiates the efficacy of EIDD-1931 and PF-332 by targeting the papain like protease enzyme of SARS-CoV-2.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 15;15(1):5671. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89717-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39955340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 3 January 2021)]; Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

