The lncRNA 44s2 Study Applicability to the Design of 45-55 Exon Skipping Therapeutic Strategy for DMD
- PMID: 33672764
- PMCID: PMC7924625
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9020219
The lncRNA 44s2 Study Applicability to the Design of 45-55 Exon Skipping Therapeutic Strategy for DMD
Abstract
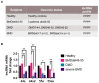
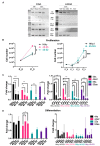
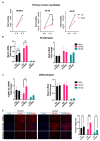
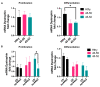
In skeletal muscle, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in dystrophin protein stabilization but also in the regulation of myocytes proliferation and differentiation. Hence, they could represent promising therapeutic targets and/or biomarkers for Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy (DMD/BMD). DMD and BMD are X-linked myopathies characterized by a progressive muscular dystrophy with or without dilatative cardiomyopathy. Two-thirds of DMD gene mutations are represented by deletions, and 63% of patients carrying DMD deletions are eligible for 45 to 55 multi-exons skipping (MES), becoming BMD patients (BMDΔ45-55). We analyzed the genomic lncRNA presence in 38 BMDΔ45-55 patients and characterized the lncRNA localized in introns 44 and 55 of the DMD gene. We highlighted that all four lncRNA are differentially expressed during myogenesis in immortalized and primary human myoblasts. In addition, the lncRNA44s2 was pointed out as a possible accelerator of differentiation. Interestingly, lncRNA44s expression was associated with a favorable clinical phenotype. These findings suggest that lncRNA44s2 could be involved in muscle differentiation process and become a potential disease progression biomarker. Based on these results, we support MES45-55 therapy and propose that the design of the CRISPR/Cas9 MES45-55 assay consider the lncRNA sequences bordering the exonic 45 to 55 deletion.
Keywords: Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD); Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD); lncRNA; long noncoding RNA; ncRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; or in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Direct Reprogramming of Human DMD Fibroblasts into Myotubes for In Vitro Evaluation of Antisense-Mediated Exon Skipping and Exons 45-55 Skipping Accompanied by Rescue of Dystrophin Expression.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1828:141-150. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8651-4_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30171539 Free PMC article.
-
Exons 45-55 Skipping Using Mutation-Tailored Cocktails of Antisense Morpholinos in the DMD Gene.Mol Ther. 2019 Nov 6;27(11):2005-2017. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.07.012. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Mol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31416775 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Multiexon Skipping by Antisense PMOs in Dystrophic Dog and Exon 7-Deleted DMD Patient.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1828:151-163. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8651-4_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30171540 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Exon Skipping in the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Hot Spots: Prospects and Challenges.J Pers Med. 2018 Dec 7;8(4):41. doi: 10.3390/jpm8040041. J Pers Med. 2018. PMID: 30544634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MLPA Analyses Reveal a Spectrum of Dystrophin Gene Deletions/Duplications in Pakistani Patients Suspected of Having Duchenne/Becker Muscular Dystrophy: A Retrospective Study.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2019 Jul;23(7):468-472. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2018.0262. Epub 2019 May 31. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2019. PMID: 31157985 Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of exons 45 to 55 in the DMD gene: from the therapeutic perspective to the in vitro model.Skelet Muscle. 2024 Oct 1;14(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13395-024-00353-3. Skelet Muscle. 2024. PMID: 39354597 Free PMC article.
-
IGFBP7 promotes the proliferation and differentiation of primary myoblasts and intramuscular preadipocytes in chicken.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104258. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104258. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39293261 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring lncRNA-Mediated Mechanisms in Muscle Regulation and Their Implications for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 24;26(13):6032. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136032. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNAs as a new regulator of chronic musculoskeletal disorder.Cell Prolif. 2021 Oct;54(10):e13113. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13113. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Cell Prolif. 2021. PMID: 34498342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Coding RNAs in Health and Disease: Editorial.Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 21;11(1):14. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11010014. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36672521 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

