Performance of Ultrasound Techniques and the Potential of Artificial Intelligence in the Evaluation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- PMID: 33672827
- PMCID: PMC7918928
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13040790
Performance of Ultrasound Techniques and the Potential of Artificial Intelligence in the Evaluation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
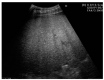
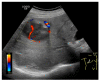
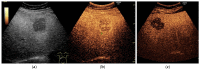
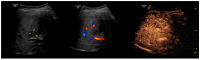
Global statistics show an increasing percentage of patients that develop non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and NAFLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), even in the absence of cirrhosis. In the present review, we analyzed the diagnostic performance of ultrasonography (US) in the non-invasive evaluation of NAFLD and NAFLD-related HCC, as well as possibilities of optimizing US diagnosis with the help of artificial intelligence (AI) assistance. To date, US is the first-line examination recommended in the screening of patients with clinical suspicion of NAFLD, as it is readily available and leads to a better disease-specific surveillance. However, the conventional US presents limitations that significantly hamper its applicability in quantifying NAFLD and accurately characterizing a given focal liver lesion (FLL). Ultrasound contrast agents (UCAs) are an essential add-on to the conventional B-mode US and to the Doppler US that further empower this method, allowing the evaluation of the enhancement properties and the vascular architecture of FLLs, in comparison to the background parenchyma. The current paper also explores the new universe of AI and the various implications of deep learning algorithms in the evaluation of NAFLD and NAFLD-related HCC through US methods, concluding that it could potentially be a game changer for patient care.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; contrast enhanced ultrasound; focal liver lesion; hepatocellular carcinoma; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; steatosis; ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

