From Data Mining of Chitinophaga sp. Genome to Enzyme Discovery of a Hyperthermophilic Metallocarboxypeptidase
- PMID: 33673011
- PMCID: PMC7918520
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9020393
From Data Mining of Chitinophaga sp. Genome to Enzyme Discovery of a Hyperthermophilic Metallocarboxypeptidase
Abstract
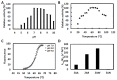
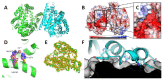
For several centuries, microorganisms and enzymes have been used for many different applications. Although many enzymes with industrial applications have already been reported, different screening technologies, methods and approaches are constantly being developed in order to allow the identification of enzymes with even more interesting applications. In our work, we have performed data mining on the Chitinophaga sp. genome, a gram-negative bacterium isolated from a bacterial consortium of sugarcane bagasse isolated from an ethanol plant. The analysis of 8 Mb allowed the identification of the chtcp gene, previously annotated as putative Cht4039. The corresponding codified enzyme, denominated as ChtCP, showed the HEXXH conserved motif of family M32 from thermostable carboxypeptidases. After expression in E. coli, the recombinant enzyme was characterized biochemically. ChtCP showed the highest activity versus benziloxicarbonil Ala-Trp at pH 7.5, suggesting a preference for hydrophobic substrates. Surprisingly, the highest activity of ChtCP observed was between 55 °C and 75 °C, and 62% activity was still displayed at 100 °C. We observed that Ca2+, Ba2+, Mn2+ and Mg2+ ions had a positive effect on the activity of ChtCP, and an increase of 30 °C in the melting temperature was observed in the presence of Co2+. These features together with the structure of ChtCP at 1.2 Å highlight the relevance of ChtCP for further biotechnological applications.
Keywords: Chitinophaga sp.; M32 family of peptidases; metallocarboxypeptidase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Metagenome-assembled genome of a Chitinophaga sp. and its potential in plant biomass degradation, as well of affiliated Pandoraea and Labrys species.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Aug 27;37(9):162. doi: 10.1007/s11274-021-03128-w. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34448059
-
Highly active metallocarboxypeptidase from newly isolated Geobacillus strain SBS-4S: cloning and characterization.J Biosci Bioeng. 2011 Mar;111(3):259-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2010.11.002. Epub 2010 Dec 3. J Biosci Bioeng. 2011. PMID: 21126910
-
Overexpression and characterization of a carboxypeptidase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus sp. NA1.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2006 May;70(5):1140-7. doi: 10.1271/bbb.70.1140. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16717414
-
Biochemical and structural characterization of a keratin-degrading M32 carboxypeptidase from Fervidobacterium islandicum AW-1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Dec 25;468(4):927-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.11.058. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26603937
-
Proteomic insights into mannan degradation and protein secretion by the forest floor bacterium Chitinophaga pinensis.J Proteomics. 2017 Mar 6;156:63-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.01.003. Epub 2017 Jan 6. J Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28069559
Cited by
-
Functional and Phylogenetic Characterization of Bacteria in Bovine Rumen Using Fractionation of Ruminal Fluid.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 25;13:813002. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.813002. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35401437 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of lake bacteria promotes human echovirus inactivation.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Feb 19;91(2):e0236624. doi: 10.1128/aem.02366-24. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39819037 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Docking of Lac_CB10: Highlighting the Great Potential for Bioremediation of Recalcitrant Chemical Compounds by One Predicted Bacteroidetes CopA-Laccase.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 6;24(12):9785. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129785. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37372934 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenome-assembled genome of a Chitinophaga sp. and its potential in plant biomass degradation, as well of affiliated Pandoraea and Labrys species.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Aug 27;37(9):162. doi: 10.1007/s11274-021-03128-w. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34448059
-
Environmentally derived Balamuthia mandrillaris contains endosymbiotic bacteria.Parasitol Res. 2025 Jun 2;124(6):57. doi: 10.1007/s00436-025-08505-0. Parasitol Res. 2025. PMID: 40455119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang J.E., Choi Y.J., Lee S.J., Kang K.-H., Lee H., Oh Y.H., Lee S.H., Park S.J., Lee S.Y. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) from glucose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014;98:95–104. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5285-z. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

