Notch Signaling Pathway in Cancer-Review with Bioinformatic Analysis
- PMID: 33673145
- PMCID: PMC7918426
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13040768
Notch Signaling Pathway in Cancer-Review with Bioinformatic Analysis
Abstract
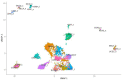
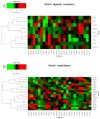
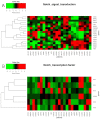
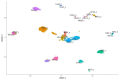
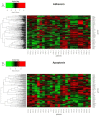
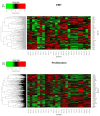
Notch signaling is an evolutionarily conserved pathway regulating normal embryonic development and homeostasis in a wide variety of tissues. It is also critically involved in carcinogenesis, as well as cancer progression. Activation of the Notch pathway members can be either oncogenic or suppressive, depending on tissue context. The present study is a comprehensive overview, extended with a bioinformatics analysis of TCGA cohorts, including breast, bladder, cervical, colon, kidney, lung, ovary, prostate and rectum carcinomas. We performed global expression profiling of the Notch pathway core components and downstream targets. For this purpose, we implemented the Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection algorithm to reduce the dimensions. Furthermore, we determined the optimal cutpoint using Evaluate Cutpoint software to established disease-free and overall survival with respect to particular Notch members. Our results demonstrated separation between tumors and their corresponding normal tissue, as well as between tumors in general. The differentiation of the Notch pathway, at its various stages, in terms of expression and survival resulted in distinct profiles of biological processes such as proliferation, adhesion, apoptosis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. In conclusion, whether oncogenic or suppressive, Notch signaling is proven to be associated with various types of malignancies, and thus may be of interest as a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: Notch signaling; carcinogenesis; global signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional Gene Expression Differentiation of the Notch Signaling Pathway in Female Reproductive Tract Tissues-A Comprehensive Review With Analysis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 15;8:592616. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.592616. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33384996 Free PMC article.
-
The Relevance of Notch Signaling in Cancer Progression.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1287:169-181. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-55031-8_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33034032 Review.
-
Notch as a tumour suppressor.Nat Rev Cancer. 2017 Mar;17(3):145-159. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.145. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28154375 Review.
-
The role of Notch signaling in gastric carcinoma: molecular pathogenesis and novel therapeutic targets.Oncotarget. 2017 May 11;8(32):53839-53853. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17809. eCollection 2017 Aug 8. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NOTCH signaling: Journey of an evolutionarily conserved pathway in driving tumor progression and its modulation as a therapeutic target.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021 Aug;164:103403. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103403. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021. PMID: 34214610 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic and Prognostic Relevance of Cancer Stem Cell Populations in Endometrial Cancer: A Narrative Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jul 25;15(15):1872. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15151872. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40804837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative Analysis of Gene Expression and Promoter Methylation to Differentiate High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer from Benign Tumors.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 11;13(2):441. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020441. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002854 Free PMC article.
-
S-Adenosylmethionine Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Migration through Mirna-Mediated Targeting of Notch Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 12;23(14):7673. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147673. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887021 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Role of Neurogenic Locus Notch Homolog Protein 1 in Oral Cancer Progression and Therapeutic Opportunities.Cureus. 2025 Jun 16;17(6):e86149. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86149. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40672020 Free PMC article.
-
Analysing potent biomarkers along phytochemicals for breast cancer therapy: an in silico approach.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan;203(1):29-47. doi: 10.1007/s10549-023-07107-7. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 37726449 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

