Impact of Plasma Oxidative Stress Markers on Post-race Recovery in Ultramarathon Runners: A Sex and Age Perspective Overview
- PMID: 33673404
- PMCID: PMC7996940
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10030355
Impact of Plasma Oxidative Stress Markers on Post-race Recovery in Ultramarathon Runners: A Sex and Age Perspective Overview
Abstract
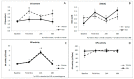
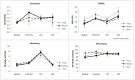
Oxidative stress has been widely studied in association to ultra-endurance sports. Although it is clearly demonstrated the increase in reactive oxygen species and free radicals after these extreme endurance exercises, the effects on the antioxidant defenses and the oxidative damage to macromolecules, remain to be fully clarified. Therefore, the aim of this study was to elucidate the impact of an ultramarathon race on the plasma markers of oxidative stress of 32 runners and their post-race recovery, with especial focused on sex and age effect. For this purpose, the antioxidant enzymes glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and glutathione reductase (GR) activity, as well as the lipid peroxidation product malondialdehyde (MDA) and the carbonyl groups (CG) content were measured before the race, in the finish line and 24 and 48 h after the race. We have reported an increase of the oxidative damage to lipids and proteins (MDA and CG) after the race and 48 h later. Moreover, there was an increase of the GR activity after the race. No changes were observed in runners' plasma GPx activity throughout the study. Finally, we have observed sex and age differences regarding damage to macromolecules, but no differences were found regarding the antioxidant enzymes measured. Our results suggest that several basal plasma markers of oxidative stress might be related to the extent of muscle damage after an ultraendurance race and also might affect the muscle strength evolution.
Keywords: antioxidants; muscle injury; oxidative stress; ultraendurance exercise.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Martínez-Navarro I., Sanchez-Gómez J.M., Aparicio I., Priego-Quesada J.I., Pérez-Soriano P., Collado E., Hernando B., Hernando C. Effect of mountain ultramarathon distance competition on biochemical variables, respiratory and lower-limb fatigue. PLoS ONE. 2020;15 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238846. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

