Biotechnological Production of the Sunscreen Pigment Scytonemin in Cyanobacteria: Progress and Strategy
- PMID: 33673485
- PMCID: PMC7997468
- DOI: 10.3390/md19030129
Biotechnological Production of the Sunscreen Pigment Scytonemin in Cyanobacteria: Progress and Strategy
Abstract
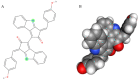
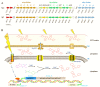
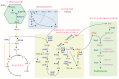
Scytonemin is a promising UV-screen and antioxidant small molecule with commercial value in cosmetics and medicine. It is solely biosynthesized in some cyanobacteria. Recently, its biosynthesis mechanism has been elucidated in the model cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme PCC 73102. The direct precursors for scytonemin biosynthesis are tryptophan and p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate, which are generated through the shikimate and aromatic amino acid biosynthesis pathway. More upstream substrates are the central carbon metabolism intermediates phosphoenolpyruvate and erythrose-4-phosphate. Thus, it is a long route to synthesize scytonemin from the fixed atmospheric CO2 in cyanobacteria. Metabolic engineering has risen as an important biotechnological means for achieving sustainable high-efficiency and high-yield target metabolites. In this review, we summarized the biochemical properties of this molecule, its biosynthetic gene clusters and transcriptional regulations, the associated carbon flux-driving progresses, and the host selection and biosynthetic strategies, with the aim to expand our understanding on engineering suitable cyanobacteria for cost-effective production of scytonemin in future practices.
Keywords: cyanobacteria; metabolic engineering; scytonemin; sunscreen pigments.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparative genomics approach to understanding the biosynthesis of the sunscreen scytonemin in cyanobacteria.BMC Genomics. 2009 Jul 24;10:336. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-336. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19630972 Free PMC article.
-
The biosynthesis of cyanobacterial sunscreen scytonemin in intertidal microbial mat communities.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2011 Aug;77(2):322-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01113.x. Epub 2011 May 12. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2011. PMID: 21501195 Free PMC article.
-
The cyanobacterial UV-absorbing pigment scytonemin displays radical-scavenging activity.J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2012;58(2):137-44. doi: 10.2323/jgam.58.137. J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22688245
-
Cyanobacterial Sunscreen Scytonemin: Role in Photoprotection and Biomedical Research.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2015 Jul;176(6):1551-63. doi: 10.1007/s12010-015-1676-1. Epub 2015 May 27. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26013282 Review.
-
Bioinspired biomolecules: Mycosporine-like amino acids and scytonemin from Lyngbya sp. with UV-protection potentialities.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019 Dec;201:111684. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111684. Epub 2019 Nov 6. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019. PMID: 31733505 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of the protective shield against UV-C radiation and its molecular interactions in Nostoc species (Cyanobacteria).Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 20;14(1):19258. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70002-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39164328 Free PMC article.
-
Sustainable Production of Pigments from Cyanobacteria.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2023;183:171-251. doi: 10.1007/10_2022_211. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36571616
-
Cyanobacteria and microalgae bioactive compounds in skin-ageing: potential to restore extracellular matrix filling and overcome hyperpigmentation.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021 Dec;36(1):1829-1838. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1960830. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34353202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Living Color: Pigment-Based Microbial Ecology At the Mineral-Air Interface.Bioscience. 2022 Oct 22;72(12):1156-1175. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biac091. eCollection 2022 Dec. Bioscience. 2022. PMID: 36451971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cosmetic Application of Cyanobacteria Extracts with a Sustainable Vision to Skincare: Role in the Antioxidant and Antiaging Process.Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 2;20(12):761. doi: 10.3390/md20120761. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36547908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zahra Z., Choo D.H., Lee H., Parveen A. Cyanobacteria: Review of current potentials and applications. Environments. 2020;7:13. doi: 10.3390/environments7020013. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

