Solanum lycopersicum Seedlings. Metabolic Responses Induced by the Alkamide Affinin
- PMID: 33673570
- PMCID: PMC7997251
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo11030143
Solanum lycopersicum Seedlings. Metabolic Responses Induced by the Alkamide Affinin
Abstract
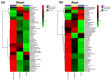
Alkamides have been observed to interact in different ways in several superior organisms and have been used in traditional medicine in many countries e.g., to relieve pain. Previous studies showed that affinin when applied to other plant species induces prominent changes in the root architecture and induces transcriptional adjustments; however, little is known about the metabolic pathways recruited by plants in response to alkamides. Previous published work with Arabidopsis seedlings treated in vitro with affinin at 50 µM significantly reduced primary root length. In tomato seedlings, that concentration did not reduce root growth but increase the number and length of lateral roots. Non-targeted metabolomic analysis by Gas Chromatography couplet to Mass Spectrometry (GC/EIMS) showed that, in tomato seedlings, affinin increased the accumulation of several metabolites leading to an enrichment of several metabolic pathways. Affinin at 100 µM alters the accumulation of metabolites such as organic acids, amino acids, sugars, and fatty acids. Finally, our results showed a response possibly associated with nitrogen, GABA shunt and serine pathways, in addition to a possible alteration in the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC), interesting topics to understand the molecular and metabolic mechanisms in response to alkamide in plants.
Keywords: Solanum lycopersicum; affinin; alkamides; gas chromatography couplet to mass spectrometry (GC/EIMS); metabolite profiling; plant immunity; tomato.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare. All co-authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript and there is no financial interest to report. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the result.
Figures





References
-
- Molinatorres J., Salgado-Garciglia R., Ramirez-Chavez E., del Rio R.E. Purely olefinic alkamnides in Heliopsis longipes and Acmella (Spilanthes) oppositifolia. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1996;24:43–47. doi: 10.1016/0305-1978(95)00099-2. - DOI
-
- Chávez E.R., Valdez L.L., Calleros G.V., Torres J.M. Actividad fungicida de la afinina y del extracto crudo de raíces de Heliopsis longipes en dos especies de Sclerotium. [(accessed on 23 October 2020)];Agrociencia. 2000 34:207–215. Available online: www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=30234210.
-
- González-Morales S., Flores López M.L., Benavides Mendoza A., Flores Olivas A. Actividad Inhibitoria del Extracto de Heliopsis longipes Sobre Fusarium oxysporum f. sp lycopersici. Rev. Mex. Fitopatol. 2011;29:146–153.
-
- Castro-Ruiz J.E., Rojas-Molina A., Luna-Vázquez F.J., Rivero-Cruz F., García-Gasca T., Ibarra-Alvarado C. Affinin (Spilanthol), Isolated from Heliopsis longipes, Induces Vasodilation via Activation of Gasotransmitters and Prostacyclin Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017;18:218. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010218. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

