Targeted Physical Therapy Combined with Spasticity Management Changes Motor Development Trajectory for a 2-Year-Old with Cerebral Palsy
- PMID: 33673573
- PMCID: PMC7997196
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm11030163
Targeted Physical Therapy Combined with Spasticity Management Changes Motor Development Trajectory for a 2-Year-Old with Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
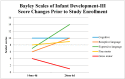
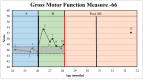
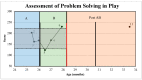
Therapies for children with cerebral palsy (CP) often fail to address essential components of early rehabilitation: intensity, child initiation, and an embodied approach. Sitting Together And Reaching To Play (START-Play) addresses these issues while incorporating intensive family involvement to maximize therapeutic dosage. While START-Play was developed and tested on children aged 7-16 months with motor delays, the theoretical construct can be applied to intervention in children of broader ages and skills levels. This study quantifies the impact of a broader START-Play intervention combined with Botulinum toxin-A (BoNT-A) and phenol on the developmental trajectory of a 24 month-old child with bilateral spastic CP. In this AB +1 study, A consisted of multiple baseline assessments with the Gross Motor Function Measure-66 and the Assessment of Problem Solving in Play. The research participant demonstrated a stable baseline during A and changes in response to the combination of BoNT-A/phenol and 12 START-Play sessions during B, surpassing the minimal clinically important difference on the Gross Motor Function Measure-66. The follow-up data point (+1) was completed after a second round of BoNT-A/phenol injections. While the findings suggest the participant improved his gross motor skills with BoNT-A/phenol and START-Play, further research is needed to generalize these findings.
Keywords: Botulinum toxin-A; cerebral palsy; early intervention; phenol; physical therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The sponsors had no role in the design, execution, interpretation, or writing of the study.
Figures

References
-
- Karch D., Heinemann K. Cerebral Palsy. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2018. Physiotherapeutic Interventions: Bobath, Vojta, and Motor Learning Approaches; pp. 155–164.
-
- Novak I., Morgan C., Fahey M., Finch-Edmondson M., Galea C., Hines A., Langdon K., Mc Namara M., Paton M.C., Popat H. State of the evidence traffic lights 2019: Systematic review of interventions for preventing and treating children with cerebral palsy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020;20:1–21. doi: 10.1007/s11910-020-1022-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

