On Broken Ne(c)ks and Broken DNA: The Role of Human NEKs in the DNA Damage Response
- PMID: 33673578
- PMCID: PMC7997185
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10030507
On Broken Ne(c)ks and Broken DNA: The Role of Human NEKs in the DNA Damage Response
Abstract
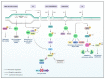
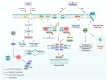
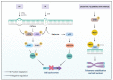
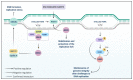
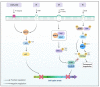
NIMA-related kinases, or NEKs, are a family of Ser/Thr protein kinases involved in cell cycle and mitosis, centrosome disjunction, primary cilia functions, and DNA damage responses among other biological functional contexts in vertebrate cells. In human cells, there are 11 members, termed NEK1 to 11, and the research has mainly focused on exploring the more predominant roles of NEKs in mitosis regulation and cell cycle. A possible important role of NEKs in DNA damage response (DDR) first emerged for NEK1, but recent studies for most NEKs showed participation in DDR. A detailed analysis of the protein interactions, phosphorylation events, and studies of functional aspects of NEKs from the literature led us to propose a more general role of NEKs in DDR. In this review, we express that NEK1 is an activator of ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR), and its activation results in cell cycle arrest, guaranteeing DNA repair while activating specific repair pathways such as homology repair (HR) and DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair. For NEK2, 6, 8, 9, and 11, we found a role downstream of ATR and ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) that results in cell cycle arrest, but details of possible activated repair pathways are still being investigated. NEK4 shows a connection to the regulation of the nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair of DNA DSBs, through recruitment of DNA-PK to DNA damage foci. NEK5 interacts with topoisomerase IIβ, and its knockdown results in the accumulation of damaged DNA. NEK7 has a regulatory role in the detection of oxidative damage to telomeric DNA. Finally, NEK10 has recently been shown to phosphorylate p53 at Y327, promoting cell cycle arrest after exposure to DNA damaging agents. In summary, this review highlights important discoveries of the ever-growing involvement of NEK kinases in the DDR pathways. A better understanding of these roles may open new diagnostic possibilities or pharmaceutical interventions regarding the chemo-sensitizing inhibition of NEKs in various forms of cancer and other diseases.
Keywords: DNA damage response; cell cycle; kinase; protein kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

