Is Inflammation a Friend or Foe for Orthodontic Treatment?: Inflammation in Orthodontically Induced Inflammatory Root Resorption and Accelerating Tooth Movement
- PMID: 33673606
- PMCID: PMC7957544
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052388
Is Inflammation a Friend or Foe for Orthodontic Treatment?: Inflammation in Orthodontically Induced Inflammatory Root Resorption and Accelerating Tooth Movement
Abstract
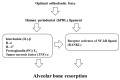
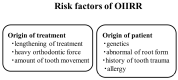
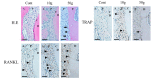
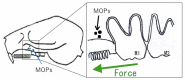
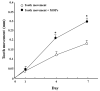
The aim of this paper is to provide a review on the role of inflammation in orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption (OIIRR) and accelerating orthodontic tooth movement (AOTM) in orthodontic treatment. Orthodontic tooth movement (OTM) is stimulated by remodeling of the periodontal ligament (PDL) and alveolar bone. These remodeling activities and tooth displacement are involved in the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the periodontium, in response to orthodontic forces. Inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins (PGs), interleukins (Ils; IL-1, -6, -17), the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α superfamily, and receptor activator of nuclear factor (RANK)/RANK ligand (RANKL)/osteoprotegerin (OPG) are increased in the PDL during OTM. OIIRR is one of the accidental symptoms, and inflammatory mediators have been detected in resorbed roots, PDL, and alveolar bone exposed to heavy orthodontic force. Therefore, these inflammatory mediators are involved with the occurrence of OIIRR during orthodontic tooth movement. On the contrary, regional accelerating phenomenon (RAP) occurs after fractures and surgery such as osteotomies or bone grafting, and bone healing is accelerated by increasing osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Recently, tooth movement after surgical procedures such as corticotomy, corticision, piezocision, and micro-osteoperforation might be accelerated by RAP, which increases the bone metabolism. Therefore, inflammation may be involved in accelerated OTM (AOTM). The knowledge of inflammation during orthodontic treatment could be used in preventing OIIRR and AOTM.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing; fabry disease; induced pluripotent stem cells; inflammatory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Davidovitch Z., Nicolay O.F., Ngan P.W., Shanfeld J.L. Neurotransmitters, cytokines, and the control of alveolar bone remodeling in orthodontics. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 1988;32:411–435. - PubMed
-
- Brezniak N., Wasserstein A. Orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption. Part II: The clinical aspects. Angle Orthod. 2002;72:180–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

