High-Intensity Interval Training and α-Linolenic Acid Supplementation Improve DHA Conversion and Increase the Abundance of Gut Mucosa-Associated Oscillospira Bacteria
- PMID: 33673609
- PMCID: PMC7997329
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13030788
High-Intensity Interval Training and α-Linolenic Acid Supplementation Improve DHA Conversion and Increase the Abundance of Gut Mucosa-Associated Oscillospira Bacteria
Abstract
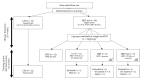
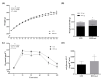
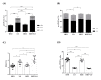
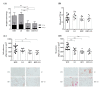
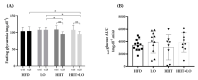
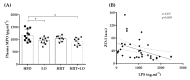
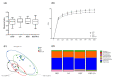
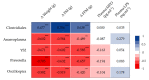
Obesity, a major public health problem, is the consequence of an excess of body fat and biological alterations in the adipose tissue. Our aim was to determine whether high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and/or α-linolenic acid supplementation (to equilibrate the n-6/n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) ratio) might prevent obesity disorders, particularly by modulating the mucosa-associated microbiota. Wistar rats received a low fat diet (LFD; control) or high fat diet (HFD) for 16 weeks to induce obesity. Then, animals in the HFD group were divided in four groups: HFD (control), HFD + linseed oil (LO), HFD + HIIT, HFD + HIIT + LO. In the HIIT groups, rats ran on a treadmill, 4 days.week-1. Erythrocyte n-3 PUFA content, body composition, inflammation, and intestinal mucosa-associated microbiota composition were assessed after 12 weeks. LO supplementation enhanced α-linolenic acid (ALA) to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) conversion in erythrocytes, and HIIT potentiated this conversion. Compared with HFD, HIIT limited weight gain, fat mass accumulation, and adipocyte size, whereas LO reduced systemic inflammation. HIIT had the main effect on gut microbiota β-diversity, but the HIIT + LO association significantly increased Oscillospira relative abundance. In our conditions, HIIT had a major effect on body fat mass, whereas HIIT + LO improved ALA conversion to DHA and increased the abundance of Oscillospira bacteria in the microbiota.
Keywords: body composition; exercise; linseed oil supplementation; microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Fact Sheet: Obesity and Overweight 2016. [(accessed on 23 March 2018)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

