Vertical Transmission of Extended-Spectrum, Beta-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae during Preterm Delivery: A Prospective Study
- PMID: 33673648
- PMCID: PMC7997221
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9030506
Vertical Transmission of Extended-Spectrum, Beta-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae during Preterm Delivery: A Prospective Study
Abstract
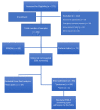
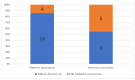
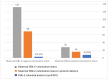
Maternal carriage and vertical transmission of extended-spectrum, beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (ESBL-E), such as Escherichia coli, hamper the treatment of infections, resulting in high morbidity. E. coli is the most frequent cause of early-onset neonatal sepsis (EOS) in preterm infants, where ESBL-E are more frequently isolated. In this prospective, case-controlled study, maternal rectovaginal ESBL-E colonization and vertical transmission to preterm infants were assessed in 160 women with preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM; 57.4%) or preterm labor (42.6%); additional cultures were obtained from the placenta, amnion, and umbilical cord during preterm labor. Maternal and neonatal ESBL-E-carriage rates were 17.5% and 12.9%, respectively, and the vertical-transmission rate was 50%. Maternal ESBL-E colonization among women with PPROM was 21.3%, and in women with premature labor it was 12.6%. No correlation was observed between maternal ESBL-E-colonization and previous hospitalization or antibiotic administration during pregnancy. However, a correlation was found between placental inflammation and maternal ESBL-E colonization (p = 0.007). ESBL-E-colonized infants were delivered at an earlier gestational age and were more likely to have complications. Thus, the high ESBL-E carriage rate in women with threatened preterm labor, without obvious risk factors for carriage, and a high vertical transmission rate, combined with a correlation between placental inflammation and ESBL-E carriage, support maternal-neonatal ESBL-E-colonization surveillance and active measures to prevent ESBL-E-related EOS.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; extended-spectrum, beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae; maternal colonization; preterm birth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal colonization with extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in term versus preterm pregnancies.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2023 May;161(2):447-454. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.14555. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2023. PMID: 36334053
-
Mother-to-child transmission of extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae.J Hosp Infect. 2018 Sep;100(1):40-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2017.12.024. Epub 2018 Jan 10. J Hosp Infect. 2018. PMID: 29330015
-
Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae among pregnant women in Norway: prevalence and maternal-neonatal transmission.J Perinatol. 2015 Nov;35(11):907-12. doi: 10.1038/jp.2015.82. Epub 2015 Jul 9. J Perinatol. 2015. PMID: 26507147
-
Maternal colonization or infection with extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Infect Dis. 2017 Nov;64:58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2017.08.015. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Int J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28890179
-
Is systematic fecal carriage screening of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae still useful in intensive care unit: a systematic review.Crit Care. 2019 May 14;23(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13054-019-2460-3. Crit Care. 2019. PMID: 31088542 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Early-Onset Infection Caused by Escherichia coli Sequence Type 1193 in Late Preterm and Full-Term Neonates.Emerg Infect Dis. 2024 Jan;30(1):20-28. doi: 10.3201/eid3001.230851. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38146959 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal Vaginal Flora in Cervical Incompetence Patients - the Impact of Escherichia coli.Reprod Sci. 2023 Oct;30(10):3010-3018. doi: 10.1007/s43032-023-01242-8. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 37118059
-
Maternal Vaginal Colonization and Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Bacteria in Vietnamese Pregnant Women.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 May 13;10(5):572. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10050572. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067975 Free PMC article.
-
Acquisition and carriage of genetically diverse multi-drug resistant gram-negative bacilli in hospitalised newborns in The Gambia.Commun Med (Lond). 2023 Jun 3;3(1):79. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00309-6. Commun Med (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37270610 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Colonization Versus Nosocomial Transmission as the Source of Drug-Resistant Bloodstream Infection in an Indian Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: A Prospective Cohort Study.Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Jul 5;77(Suppl 1):S38-S45. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciad282. Clin Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37406039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chawanpaiboon S., Vogel J.P., Moller A.-B., Lumbiganon P., Petzold M., Hogan D., Landoulsi S., Jampathong N., Kongwattanakul K., Laopaiboon M., et al. Global, regional, and national estimates of levels of preterm birth in 2014: A systematic review and modelling analysis. Lancet Glob. Health. 2019;7:e37–e46. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30451-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhutta Z.A., Chopra M., Axelson H., Berman P., Boerma T., Bryce J., Bustreo F., Cavagnero E., Cometto G., Daelmans B., et al. Countdown to 2015 decade report (2000–10): Taking stock of maternal, newborn, and child survival. Lancet. 2010;375:2032–2044. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60678-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

