Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Skin Regeneration and Rejuvenation
- PMID: 33673711
- PMCID: PMC7957487
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052410
Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Skin Regeneration and Rejuvenation
Abstract
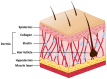
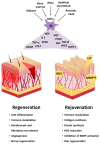
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent stem cells derived from adult stem cells. Primary MSCs can be obtained from diverse sources, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood. Recently, MSCs have been recognized as therapeutic agents for skin regeneration and rejuvenation. The skin can be damaged by wounds, caused by cutting or breaking of the tissue, and burns. Moreover, skin aging is a process that occurs naturally but can be worsened by environmental pollution, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, alcohol consumption, tobacco use, and undernourishment. MSCs have healing capacities that can be applied in damaged and aged skin. In skin regeneration, MSCs increase cell proliferation and neovascularization, and decrease inflammation in skin injury lesions. In skin rejuvenation, MSCs lead to production of collagen and elastic fibers, inhibition of metalloproteinase activation, and promote protection from ultraviolet radiation-induced senescence. In this review, we focus on how MSCs and MSC-derived molecules improve diseased and aged skin. Additionally, we emphasize that induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived MSCs are potentially advanced MSCs, which are suitable for cell therapy.
Keywords: antiaging; induced pluripotent stem cell; mesenchymal stem cells; skin regeneration; skin rejuvenation; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Viswanathan S., Shi Y., Galipeau J., Krampera M., Leblanc K., Martin I., Nolta J., Phinney D.G., Sensebe L. Mesenchymal stem versus stromal cells: International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy (ISCT®) mesenchymal stromal cell committee position statement on nomenclature. Cytotherapy. 2019;21:1019–1024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical