Factors associated with the nutritional status of the older population in a selected area of Dhaka, Bangladesh
- PMID: 33673811
- PMCID: PMC7934473
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-021-02068-2
Factors associated with the nutritional status of the older population in a selected area of Dhaka, Bangladesh
Abstract
Background: Globally, older population (aged ≥60 years) comprise 11% of the total population, and 23% of them are malnourished. Lack of knowledge and education, adverse dietary habits, depression or psychological disorders, poor oral and dental health, disability, and diseases are the reported factors responsible for malnutrition among them. Geriatric people comprise 7.5% of the total population of Bangladesh, and almost a quarter are malnourished. But there is scarce data on the factors associated with the nutritional status of the older population in Bangladesh.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among 125 older individuals (male 59, female 66) living in three villages of Uttarkhan, Dhaka, Bangladesh, to identify the factors associated with their nutritional status. The Mini Nutritional Assessment scale, Geriatric Depression Scale-Short Form, and Geriatric Oral Health Assessment Index were used for assessing the nutritional status, mental health status, and oral health quality of the respondents, respectively. Information on socio-demographic characteristics, comorbidities and dietary factors, and food behaviors were gathered by a pretested semi-structured questionnaire. Ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
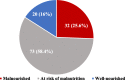
Results: The participants' mean age was 67.9 ± 7.1 years. Most of them (53.6%) had no formal education. Among the respondents, 22.0% male and 28.8% female were malnourished. The proportion of malnourished and at risk of malnutrition among the respondents living without a partner were 28.6 and 65.3%, respectively. A significantly (p < 0.05) higher odds of having depression (OR 15.6; 95% CI 3.1-78.1), poor oral health (OR 7.3; 95% CI 1.3-41.8), and no formal education (OR 6.5; 95% CI 1.3-32.1) was observed among the malnourished respondents. Though it was not statistically significant, among the malnourished, 31.3, 25.0 and 25.0% avoided highly oily food, beef/mutton, and sugary food, respectively.
Conclusions: More than two-thirds of the older population were malnourished or at risk of malnutrition, where the female respondents were more vulnerable. Depression, inadequate oral health, and lack of education were negatively associated with the nutritional status of the older population.
Keywords: Bangladesh; Geriatric Oral health assessment index; Geriatric depression scale-short form; Malnutrition; Mini nutritional assessment; Older population.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Malnutrition and other risk factors of geriatric depression: a community-based comparative cross-sectional study in older adults in rural Bangladesh.BMC Geriatr. 2021 Oct 18;21(1):572. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02535-w. BMC Geriatr. 2021. PMID: 34663237 Free PMC article.
-
Mini Nutritional Assessment and physical function of older people in residential aged care facility, Bangladesh.Nutr Health. 2022 Sep;28(3):443-452. doi: 10.1177/02601060211030119. Epub 2021 Jul 11. Nutr Health. 2022. PMID: 34250851
-
The multidimensional background of malnutrition among rural older individuals in Bangladesh--a challenge for the Millennium Development Goal.Public Health Nutr. 2009 Dec;12(12):2270-8. doi: 10.1017/S1368980009005096. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Public Health Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19257922
-
Association of Oral Health and Mini Nutritional Assessment in Older Adults: A Systematic Review with Meta-analyses.J Prosthodont Res. 2022 Apr 27;66(2):208-220. doi: 10.2186/jpr.JPR_D_20_00207. Epub 2021 Jul 15. J Prosthodont Res. 2022. PMID: 34261845
-
Health concerns regarding malnutrition among the older populations: considerations from a Slovenian perspective.Health Promot Int. 2022 Feb 17;37(1):daab097. doi: 10.1093/heapro/daab097. Health Promot Int. 2022. PMID: 34179974 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Oral and General Health with Nutritional Status of Older Adults Attending Two Medical Centers in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 18;15(18):4032. doi: 10.3390/nu15184032. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764815 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and factors associated with malnutrition on patients with cancer in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Public Health. 2024 Mar 25;2(1):e000337. doi: 10.1136/bmjph-2023-000337. eCollection 2024 Jun. BMJ Public Health. 2024. PMID: 40018103 Free PMC article.
-
Depression level, nutritional status, and dietary nutrient intake of the older adult at the community level in a selected area of Bangladesh.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 13;9(7):e18199. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18199. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37501974 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional status of older adults in India: An exploration of the role of oral health and food insecurity factors.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 14;9(10):e21028. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21028. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37886784 Free PMC article.
-
[Sociodemographic characteristics associated with underweight and overweight in adults aged 50 years and over (ELSI-Brasil): differences between sexes].Cad Saude Publica. 2024 Feb 2;40(1):e00037023. doi: 10.1590/0102-311XPT037023. eCollection 2024. Cad Saude Publica. 2024. PMID: 38324866 Free PMC article. Portuguese.
References
-
- Haque MM, Uddin AKMM, Abu Naser M, Khan MZH, Roy SK, Arafat Y. Health and nutritional status of aged people. Chattagram Maa-O-Shishu Hosp Med Coll J. 2014;13:30–34. doi: 10.3329/cmoshmcj.v13i3.21019. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization. Nutrition for health and development: a global agenda for combating malnutrition. No. WHO/NHD/00.6. World Health Organization; 2000. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/66509/WHO_NHD_00.6.pdf.
-
- United Nations . World population ageing 2017. 2017.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical