A thematic study: impact of COVID-19 pandemic on rare disease organisations and patients across ten jurisdictions in the Asia Pacific region
- PMID: 33673852
- PMCID: PMC7935006
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-021-01766-9
A thematic study: impact of COVID-19 pandemic on rare disease organisations and patients across ten jurisdictions in the Asia Pacific region
Abstract
Background: This study assesses the areas and extent of impact of the Coronavirus Disease of 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on rare disease (RD) organisations in the Asia Pacific region. There is no existing literature that focuses on such impact on RD organisations in any jurisdictions, nor RD populations across multiple jurisdictions in the Asia Pacific region. A cross-sectional survey was distributed to RD organisations between April and May 2020. Quantitative and qualitative data on the impact of COVID-19 on RD organisations and patients were collected from the organisation representative's perspective. Qualitative data was analysed using thematic analysis. A follow-up focus group meeting was conducted in August 2020 to validate the survey findings and to discuss specific needs, support and recommendations for sustainable healthcare systems during the pandemic.
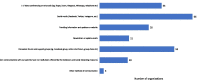
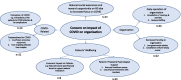
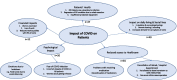
Results: A total of 80 RD organisations from Australia, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of China, India, Japan, mainland China, Malaysia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore and Taiwan participated in the study. Of all, 89% were concerned about the impact of pandemic on their organisations. Results indicate that 63% of the organisations functioned at a reduced capacity and 42% stated a decrease in funding as their biggest challenge. Overall, 95% believed their patients were impacted, particularly in healthcare access, social lives, physical health, psychological health and financial impact. Specifically, 43% identified the reduced healthcare access as their top impact, followed by 26% about the impact on daily living and social life. Focus group meeting discussed differential impact across jurisdictions and point towards telemedicine and digitalisation as potential solutions.
Conclusions: This serves as the first study to assess the impact of COVID-19 on RD patients and organisations across multiple jurisdictions in the Asia Pacific region, identifying major themes on the impact on both RD patients and organisations. By including 80 organisations from ten jurisdictions, our study presents the most comprehensive assessment of the pandemic's impact to date. It highlights the need for mental health support and sheds light on moving towards telemedicine and digitalisation of organisation operation, which constitutes a sustainable model in times of pandemics and beyond.
Keywords: Asia Pacific; COVID-19; Rare disease; Rare disease organisation; Rare disease patients; Thematic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Elflein J. COVID-19 cases worldwide by day. 2020. Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1103040/cumulative-coronavirus-covid.... Accessed 17 Sept 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion. Available from: https://www.who.int/medicines/areas/priority_medicines/Ch6_19Rare.pdf. Accessed 17 Sept 2020.
-
- European Patients Forum. What is a patient organisation? Available from: https://www.eu-patient.eu/members/what-is-a-patient-organisation/
-
- Orphanet: Patient organisation. Available from: https://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/SupportGroup_Search.php?lng=EN. Accessed 8 Jan 2021
-
- United Nations sexual and reproductive health agency. Population trends. Available from: https://asiapacific.unfpa.org/en/node/15207. Published August 21, 2015. Accessed 17 Sept 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous