A Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Study of Intravenous Midazolam and Flumazenil in Adult New Zealand White-Californian Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus)
- PMID: 33673881
- PMCID: PMC8145127
- DOI: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-20-000084
A Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Study of Intravenous Midazolam and Flumazenil in Adult New Zealand White-Californian Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus)
Abstract
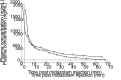
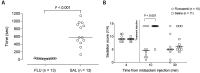
Flumazenil, a competitive GABAA receptor antagonist, is commonly used in rabbits to shorten sedation or postanesthetic recovery after benzodiazepine administration. However, no combined pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) data are available to guide its administration in this species. In a prospective, randomized, blinded, crossover study design, the efficacy of IV flumazenil (FLU; 0.05 mg/kg) or saline control (SAL; equal volume) to reverse the loss of righting reflex (LORR) induced by IV midazolam (1.2 mg/kg) was investigated in 15 New Zealand white rabbits (2.73 to 4.65 kg, 1 y old). Rabbits were instrumented with arterial (central auricular artery) and venous (marginal auricular vein) catheters. After baseline blood sampling, IV midazolam was injected (T0). Flumazenil or saline (FLU/SAL) was injected 30 s after LORR. Arterial blood samples were collected at 1 and 3 min after midazolam injection, and at 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 28, 36, 45 and 60 min after injection with flumazenil. Plasma samples for midazolam, 1-OH-midazolam and flumazenil were analyzed using high performance liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry and the time to return of righting reflex (ReRR) was compared between groups (Wilcoxon test). FLU terminal half-life, plasma clearance and volume of distribution were 26.3 min [95%CI: 23.3 to 29.3], 18.74 mL/min/kg [16.47 to 21.00] and 0.63 L/kg [0.55 to 0.71], respectively. ReRR was 25 times faster in rabbits treated with FLU (23 [8 to 44] s) compared with SAL (576 [130 to 1141] s; 95%CI [425 to 914 s]). Return of sedation (lateral recumbency) occurred in both groups (7/13 in FLU; 12/13 in SAL) with return of LORR in a few animals (4/13 in FLU; 7/13 in SAL) at 1540 [858 to 2328] s. In the population and anesthesia protocol studied, flumazenil quickly and reliably reversed sedation induced by midazolam injection. However, the potential return of sedation after flumazenil administration warrants careful monitoring in the recovery period.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Intramuscular Alfaxalone-Butorphanol-Midazolam Compared with Ketamine-Butorphanol- Midazolam in New Zealand White Rabbits.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2022 Sep 1;61(5):475-481. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-22-000038. Epub 2022 Aug 26. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 36028310 Free PMC article.
-
Physostigmine reversal of midazolam-induced electroencephalographic changes in healthy subjects.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000 May;67(5):538-48. doi: 10.1067/mcp.2000.105988. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000. PMID: 10824633 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of flumazenil on recovery after midazolam and propofol sedation.Anesthesiology. 1994 Aug;81(2):333-9. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199408000-00010. Anesthesiology. 1994. PMID: 8053582 Clinical Trial.
-
A pilot pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study of benzodiazepine antagonism by flumazenil and aminophylline.Pharmacotherapy. 1996 Nov-Dec;16(6):1166-72. Pharmacotherapy. 1996. PMID: 8947991 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of flumazenil on ventilatory drive during sedation with midazolam and alfentanil.Anesthesiology. 1996 Oct;85(4):713-20. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199610000-00005. Anesthesiology. 1996. PMID: 8873540 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Aarseth HP, Bredesen JE, Grynne B, Lyngdal PT, Storstein L, Wiik-Larsen E. 1988. Benzodiazepine-receptor antagonist, a clinical double-blind study. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 26:283–292. - PubMed
-
- Avsaroglu H. [Internet]. 2008. Strain specific response to anaesthetics and analgesics in rat and rabbit. A pharmacogenetic approach. (PhD Dissertation). ISBN: 978-90-393-4884-0. Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands. [Cited 01 November 2020]. Available at: https://dspace.library.uu.nl/handle/1874/29929
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

