Using artificial intelligence to improve COVID-19 rapid diagnostic test result interpretation
- PMID: 33674422
- PMCID: PMC7999948
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2019893118
Using artificial intelligence to improve COVID-19 rapid diagnostic test result interpretation
Abstract
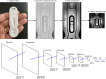
Serological rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) are widely used across pathologies, often providing users a simple, binary result (positive or negative) in as little as 5 to 20 min. Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, new RDTs for identifying SARS-CoV-2 have rapidly proliferated. However, these seemingly easy-to-read tests can be highly subjective, and interpretations of the visible "bands" of color that appear (or not) in a test window may vary between users, test models, and brands. We developed and evaluated the accuracy/performance of a smartphone application (xRCovid) that uses machine learning to classify SARS-CoV-2 serological RDT results and reduce reading ambiguities. Across 11 COVID-19 RDT models, the app yielded 99.3% precision compared to reading by eye. Using the app replaces the uncertainty from visual RDT interpretation with a smaller uncertainty of the image classifier, thereby increasing confidence of clinicians and laboratory staff when using RDTs, and creating opportunities for patient self-testing.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; machine learning; smartphone application.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang K., et al., The application of lateral flow immunoassay in point of care testing: A review. Nano Biomed. Eng. 8, 172–183 (2016).
-
- Long Q. X., et al., Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 26, 845–848 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Liu Y., et al., Diagnostic indexes of a rapid IgG/IgM combined antibody test for SARS-CoV-2. medRxiv [Preprint] (2020). 10.1101/2020.03.26.20044883 (Accessed 2 March 2021). - DOI
-
- van Amerongen A., Veen J., Arends H. A., Koets M., “Lateral flow immunoassays” in Handbook of Immunoassay Technologies, Vashist S. K., Luong J. H. T., Eds. (Academic Press, 2018), pp. 157–182.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

