Effective Antibacterial and Antihemolysin Activities of Ellipticine Hydrochloride against Streptococcus suis in a Mouse Model
- PMID: 33674433
- PMCID: PMC8117749
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03165-20
Effective Antibacterial and Antihemolysin Activities of Ellipticine Hydrochloride against Streptococcus suis in a Mouse Model
Abstract
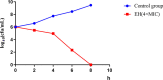
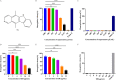
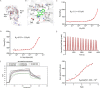
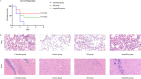
Streptococcal toxic shock-like syndrome (STSLS) caused by the epidemic strain of Streptococcus suis leads to severe inflammation and high mortality. The life and health of humans and animals are also threatened by the increasingly severe antimicrobial resistance in Streptococcus suis There is an urgent need to discover novel strategies for the treatment of S. suis infection. Suilysin (SLY) is considered to be an important virulence factor in the pathogenesis of S. suis In this study, ellipticine hydrochloride (EH) was reported as a compound that antagonizes the hemolytic activity of SLY. In vitro, EH was found to effectively inhibit SLY-mediated hemolytic activity. Furthermore, EH had a strong affinity for SLY, thereby directly binding to SLY to interfere with the hemolytic activity. Meanwhile, it was worth noting that EH was also found to have a significant antibacterial activity. In vivo, compared with traditional ampicillin, EH not only significantly improved the survival rate of mice infected with S. suis 2 strain Sc19 but also relieved lung pathological damage. Furthermore, EH effectively decreased the levels of inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-6 [IL-6], tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]) and blood biochemistry enzymes (alanine transaminase [ALT], aspartate transaminase [AST], creatine kinase [CK]) in Sc19-infected mice. Additionally, EH markedly reduced the bacterial load of tissues in Sc19-infected mice. In conclusion, our findings suggest that EH can be a potential compound for treating S. suis infection in view of its antibacterial and antihemolysin activity.IMPORTANCE In recent years, the inappropriate use of antibiotics has unnecessarily caused the continuous emergence of resistant bacteria. The antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus suis has also become an increasingly serious problem. Targeting virulence can reduce the selective pressure of bacteria on antibiotics, thereby alleviating the development of bacterial resistance to a certain extent. Meanwhile, the excessive inflammatory response caused by S. suis infection is considered the primary cause of acute death. Here, we found that ellipticine hydrochloride (EH) exhibited effective antibacterial and antihemolysin activities against S. suisin vitroIn vivo, compared with ampicillin, EH had a significant protective effect on S. suis serotype 2 strain Sc19-infected mice. Our results indicated that EH, with dual antibacterial and antivirulence effects, will contribute to treating S. suis infections and alleviating the antimicrobial resistance of S. suis to a certain extent. More importantly, EH may develop into a promising drug for the prevention of acute death caused by excessive inflammation.
Keywords: Streptococcus suis; antibacterial; antihemolysin; ellipticine hydrochloride; suilysin.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- Segura M, Zheng H, de Greeff A, Gao GF, Grenier D, Jiang Y, Lu C, Maskell D, Oishi K, Okura M, Osawa R, Schultsz C, Schwerk C, Sekizaki T, Smith H, Srimanote P, Takamatsu D, Tang J, Tenenbaum T, Tharavichitkul P, Hoa NT, Valentin-Weigand P, Wells JM, Wertheim H, Zhu B, Gottschalk M, Xu J. 2014. Latest developments on Streptococcus suis: an emerging zoonotic pathogen: part 1. Future Microbiol 9:441–444. 10.2217/fmb.14.14. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tohya M, Arai S, Tomida J, Watanabe T, Kawamura Y, Katsumi M, Ushimizu M, Ishida-Kuroki K, Yoshizumi M, Uzawa Y, Iguchi S, Yoshida A, Kikuchi K, Sekizaki T. 2017. Defining the taxonomic status of Streptococcus suis serotype 33: the proposal for Streptococcus ruminantium sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:3660–3665. 10.1099/ijsem.0.002204. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

