MINFLUX nanometer-scale 3D imaging and microsecond-range tracking on a common fluorescence microscope
- PMID: 33674570
- PMCID: PMC7935904
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21652-z
MINFLUX nanometer-scale 3D imaging and microsecond-range tracking on a common fluorescence microscope
Abstract
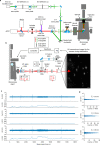
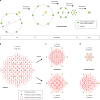
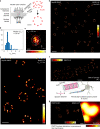
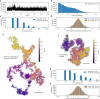
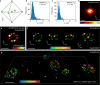
The recently introduced minimal photon fluxes (MINFLUX) concept pushed the resolution of fluorescence microscopy to molecular dimensions. Initial demonstrations relied on custom made, specialized microscopes, raising the question of the method's general availability. Here, we show that MINFLUX implemented with a standard microscope stand can attain 1-3 nm resolution in three dimensions, rendering fluorescence microscopy with molecule-scale resolution widely applicable. Advances, such as synchronized electro-optical and galvanometric beam steering and a stabilization that locks the sample position to sub-nanometer precision with respect to the stand, ensure nanometer-precise and accurate real-time localization of individually activated fluorophores. In our MINFLUX imaging of cell- and neurobiological samples, ~800 detected photons suffice to attain a localization precision of 2.2 nm, whereas ~2500 photons yield precisions <1 nm (standard deviation). We further demonstrate 3D imaging with localization precision of ~2.4 nm in the focal plane and ~1.9 nm along the optic axis. Localizing with a precision of <20 nm within ~100 µs, we establish this spatio-temporal resolution in single fluorophore tracking and apply it to the diffusion of single labeled lipids in lipid-bilayer model membranes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests. The Max Planck Society holds patents on MINFLUX. R.S., T.W., C.A.W., and I.J. are employees of Abberior Instruments manufacturing MINFLUX microscopes. C.A.W. and J.R. are employees of Abberior commercializing fluorophores for super resolution. C.A.W. and S.W.H. hold shares of Abberior Instruments, S.W.H. also of Abberior. S.J.S. declares no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

