Validity and reliability of the 'Isometric Exercise Scale' (IES) for measuring ratings of perceived exertion during continuous isometric exercise
- PMID: 33674722
- PMCID: PMC7970867
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-84803-8
Validity and reliability of the 'Isometric Exercise Scale' (IES) for measuring ratings of perceived exertion during continuous isometric exercise
Abstract
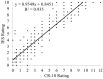
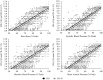
Isometric exercise (IE) interventions are an effective non-medical method of reducing arterial blood pressure (BP). Current methods of prescribing and controlling isometric exercise intensity often require the use of expensive equipment and specialist knowledge. However, ratings of perceived exertion (RPE) may provide a more accessible means of monitoring exercise intensity. Therefore, the aim of this study was to assess the validity of a specific Isometric Exercise Scale (IES) during a continuous incremental IE test. Twenty-nine male participants completed four incremental isometric wall squat tests. Each test consisted of five 2-min stages of progressively increasing workload. Workload was determined by knee joint angle from 135° to 95°. The tests were continuous with no rest periods between the stages. Throughout the exercise protocol, RPE (IES and Borg's CR-10), heart rate and blood pressure were recorded. A strong positive linear relationship was found between the IES and the CR-10 (r = 0.967). Likewise, strong positive relationships between the IES and wall squat duration (r = 0.849), HR (r = 0.819) and BP (r = 0.841) were seen. Intra-class correlation coefficients and coefficients of variations for the IES ranged from r = 0.81 to 0.91 and 4.5-54%, respectively, with greater reliability seen at the higher workloads. The IES provides valid and reliable measurements of RPE, exercise intensity, and the changes in physiological measures of exertion during continuous incremental IE; as such, the IES can be used as an accessible measure of exercise intensity during IE interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Mancia G, et al. ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur. Heart J. 2013;34:2159–2219. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht151. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

