Molecular disruption of DNA polymerase β for platinum sensitisation and synthetic lethality in epithelial ovarian cancers
- PMID: 33674744
- PMCID: PMC8032555
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-021-01710-y
Molecular disruption of DNA polymerase β for platinum sensitisation and synthetic lethality in epithelial ovarian cancers
Abstract
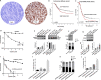
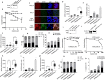
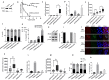
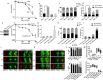
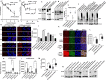
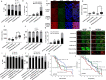
Targeting PARP1 [Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1] for synthetic lethality is a new strategy for BRCA germ-line mutated or platinum sensitive ovarian cancers. However, not all patients respond due to intrinsic or acquired resistance to PARP1 inhibitor. Development of alternative synthetic lethality approaches is a high priority. DNA polymerase β (Polβ), a critical player in base excision repair (BER), interacts with PARP1 during DNA repair. Here we show that polβ deficiency is a predictor of platinum sensitivity in human ovarian tumours. Polβ depletion not only increased platinum sensitivity but also reduced invasion, migration and impaired EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) of ovarian cancer cells. Polβ small molecular inhibitors (Pamoic acid and NSC666719) were selectively toxic to BRCA2 deficient cells and associated with double-strand breaks (DSB) accumulation, cell cycle arrest and increased apoptosis. Interestingly, PARG [Poly(ADP-Ribose) Glycohydrolase] inhibitor (PDD00017273) [but not PARP1 inhibitor (Olaparib)] was synthetically lethal in polβ deficient cells. Selective toxicity to PDD00017273 was associated with poly (ADP-ribose) accumulation, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) level, DSB accumulation, cell cycle arrest and increased apoptosis. In human tumours, polβ-PARG co-expression adversely impacted survival in patients. Our data provide evidence that polβ targeting is a novel strategy and warrants further pharmaceutical development in epithelial ovarian cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Moore K, Colombo N, Scambia G, Kim BG, Oaknin A, Friedlander M, et al. Maintenance olaparib in patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2495–505. - PubMed
-
- Mirza MR, Monk BJ, Herrstedt J, Oza AM, Mahner S, Redondo A, et al. Niraparib maintenance therapy in platinum-sensitive, recurrent ovarian cancer. N. Engl J Med. 2016;375:2154–64. - PubMed
-
- Swisher EM, Lin KK, Oza AM, Scott CL, Giordano H, Sun J, et al. Rucaparib in relapsed, platinum-sensitive high-grade ovarian carcinoma (ARIEL2 Part 1): an international, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:75–87. - PubMed
-
- D’Andrea AD. Mechanisms of PARP inhibitor sensitivity and resistance. DNA Repair. 2018;7:172–6. - PubMed
-
- Lindahl T. Repair of intrinsic DNA lesions. Mutat Res. 1990;238:305–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

