Multicentric phase II trial of TI-CE high-dose chemotherapy with therapeutic drug monitoring of carboplatin in patients with relapsed advanced germ cell tumors
- PMID: 33675184
- PMCID: PMC7982623
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3687
Multicentric phase II trial of TI-CE high-dose chemotherapy with therapeutic drug monitoring of carboplatin in patients with relapsed advanced germ cell tumors
Abstract
Background: High-dose chemotherapy (HDCT) with TI-CE regimen is a valid option for the treatment of relapsed advanced germ cell tumors (GCT). We report a phase II trial with therapeutic drug monitoring of carboplatin for optimizing area under the curve (AUC) of this drug.
Methods: Patients with unfavorable relapsed GCT were treated according to TI-CE regimen: two cycles combining paclitaxel and ifosfamide followed by three cycles of HD carboplatin plus etoposide administered on 3 days. Carboplatin dose was adapted on day 3 based on carboplatin clearance (CL) at day 1 in order to reach a target AUC of 24 mg.min/mL per cycle. The primary endpoint was the complete response (CR) rate.
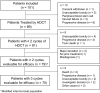
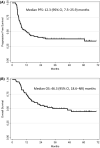
Results: Eighty-nine patients who received HDCT were included in the modified intent-to-treat (mITT) analysis. Measured mean AUC was 24.4 mg.min/mL per cycle (22.4 and 26.8 mg.min/mL for 10th and 90th percentiles). Thirty-five (44.3%) patients achieved a CR with or without surgery of residual masses and 20 patients achieved a partial response with negative tumor markers. With a median follow-up of 44 months (m), median PFS was 12.3 m (95% CI: 7.5-25.9) and OS was 46.3 m (95% CI: 18.6-not reached). For high- and very high-risk patients, according to the International Prognostic Score at first relapse or treated after at least one salvage treatment (n = 51), 2-year PFS rate was 41.1%.
Conclusion: The rates of complete and favorable responses were clinically relevant in this very poor risk population. Individual monitoring of carboplatin plasma concentration permitted to control more accurately the target AUC and avoided both underexposure and overexposure to the drug.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00864318.
Keywords: germ cell tumors; high-dose chemotherapy; phase II trial; relapsed patients; therapeutic drug monitoring.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest related to this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A phase II trial of high-dose chemotherapy (HDCT) supported by hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) in germ-cell tumors (GCTs) patients failing cisplatin-based chemotherapy: the Multicentric TAXIF II study.Ann Oncol. 2014 Sep;25(9):1775-1782. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu198. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Ann Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24894084 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I/II Trial of Paclitaxel With Ifosfamide Followed by High-Dose Paclitaxel, Ifosfamide, and Carboplatin (TI-TIC) With Autologous Stem Cell Reinfusion for Salvage Treatment of Germ Cell Tumors.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2015 Oct;13(5):453-60. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2015.05.003. Epub 2015 May 16. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26072101 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sequential dose-intensive paclitaxel, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide salvage therapy for germ cell tumor patients.J Clin Oncol. 2000 Mar;18(6):1173-80. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2000.18.6.1173. J Clin Oncol. 2000. PMID: 10715285 Clinical Trial.
-
High-dose chemotherapy for relapsed germ cell tumours: outcomes in low-volume specialized centres.BJU Int. 2022 Jun;130 Suppl 1:5-16. doi: 10.1111/bju.15648. Epub 2022 Mar 31. BJU Int. 2022. PMID: 35355402 Review.
-
Treatment of relapsed/refractory germ cell tumours: an equipoise between conventional and high dose therapy.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2012 Jun;13(2):201-11. doi: 10.1007/s11864-012-0199-z. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22623055 Review.
Cited by
-
Ototoxicity associated with high-dose carboplatin for patients with previously treated germ cell tumors.Cancer. 2023 Dec 15;129(24):3952-3961. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34991. Epub 2023 Sep 16. Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37715631 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic drug monitoring in oncology - What's out there: A bibliometric evaluation on the topic.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 10;12:959741. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.959741. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36439413 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted drug monitoring in oncology for personalized treatment with use of next generation analytics.Discov Oncol. 2025 Aug 11;16(1):1523. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03376-4. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40788512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoietic stem cell mobilization strategies to support high-dose chemotherapy: A focus on relapsed/refractory germ cell tumors.World J Clin Oncol. 2021 Sep 24;12(9):746-766. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i9.746. World J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34631440 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Einhorn LH, Williams SD, Chamness A, Brames MJ, Perkins SM, Abonour R. High‐dose chemotherapy and stem‐cell rescue for metastatic germ‐cell tumors. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:340‐348. - PubMed
-
- Rick O, Bokemeyer C, Beyer J, et al. Salvage treatment with paclitaxel, ifosfamide, and cisplatin plus high‐dose carboplatin, etoposide, and thiotepa followed by autologous stem‐cell rescue in patients with relapsed or refractory germ cell cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:81‐88. - PubMed
-
- Rodenhuis S, de Wit R, de Mulder P, et al. A multi‐center prospective phase II study of high‐dose chemotherapy in germ‐cell cancer patients relapsing from complete remission. Ann Oncol. 1999;10:1467‐1473. - PubMed
-
- Lotz J‐P, Bui B, Gomez F, et al. Sequential high‐dose chemotherapy protocol for relapsed poor prognosis germ cell tumors combining two mobilization and cytoreductive treatments followed by three high‐dose chemotherapy regimens supported by autologous stem cell transplantation. Results of the phase II multicentric TAXIF trial. Ann Oncol. 2005;16:411‐418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

