Characteristics of the MACS/WIHS Combined Cohort Study: Opportunities for Research on Aging With HIV in the Longest US Observational Study of HIV
- PMID: 33675224
- PMCID: PMC8484936
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwab050
Characteristics of the MACS/WIHS Combined Cohort Study: Opportunities for Research on Aging With HIV in the Longest US Observational Study of HIV
Abstract
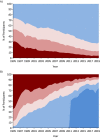
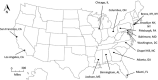
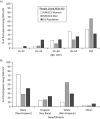
In 2019, the National Institutes of Health combined the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS) and the Women's Interagency HIV Study (WIHS) into the MACS/WIHS Combined Cohort Study (MWCCS). In this paper, participants who made a study visit during October 2018-September 2019 (targeted for MWCCS enrollment) are described by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) serostatus and compared with people living with HIV (PLWH) in the United States. Participants include 2,115 women and 1,901 men with a median age of 56 years (interquartile range, 48-63); 62% are PLWH. Study sites encompass the South (18%), the Mid-Atlantic/Northeast (45%), the West Coast (22%), and the Midwest (15%). Participant race/ethnicity approximates that of PLWH throughout the United States. Longitudinal data and specimens collected for 35 years (men) and 25 years (women) were combined. Differences in data collection and coding were reviewed, and key risk factor and comorbidity data were harmonized. For example, recent use of alcohol (62%) and tobacco (28%) are common, as are dyslipidemia (64%), hypertension (56%), obesity (42%), mildly or severely impaired daily activities (31%), depressive symptoms (28%), and diabetes (22%). The MWCCS repository includes serum, plasma, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, cell pellets, urine, cervicovaginal lavage samples, oral samples, B-cell lines, stool, and semen specimens. Demographic differences between the MACS and WIHS can confound analyses by sex. The merged MWCCS is both an ongoing observational cohort study and a valuable resource for harmonized longitudinal data and specimens for HIV-related research.
Keywords: HIV; MACS/WIHS Combined Cohort Study; Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study; Women’s Interagency HIV Study; biorepositories; cohort studies; collaborative research; comorbidity.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health 2021. This work is written by (a) US Government employee(s) and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among People Living With HIV Compared With People Without HIV: Survey Results From the MACS-WIHS Combined Cohort Study.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2022 Jan 1;89(1):1-8. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002822. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2022. PMID: 34878431 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 symptoms and SARS-CoV-2 infection among people living with HIV in the US: the MACS/WIHS combined cohort study.HIV Res Clin Pract. 2020 Oct;21(5):130-139. doi: 10.1080/25787489.2020.1844521. Epub 2020 Nov 19. HIV Res Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 33211636 Free PMC article.
-
Study of Treatment and Reproductive Outcomes Among Reproductive-Age Women With HIV Infection in the Southern United States: Protocol for a Longitudinal Cohort Study.JMIR Res Protoc. 2021 Dec 20;10(12):e30398. doi: 10.2196/30398. JMIR Res Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34932006 Free PMC article.
-
Gender differences and sex-specific manifestations associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection in women.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2003 Aug 15;109(2):199-205. doi: 10.1016/s0301-2115(03)00048-4. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2003. PMID: 12860342 Review.
-
HIV and Aging Research in Women: An Overview.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2016 Dec;13(6):383-391. doi: 10.1007/s11904-016-0338-4. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2016. PMID: 27771876 Review.
Cited by
-
Substance Use Treatment Utilization Among Women With and Without Human Immunodeficiency Virus.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022 Dec 21;10(1):ofac684. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac684. eCollection 2023 Jan. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36655189 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of syndemic heavy drinking, smoking, and depression on mortality among MSM with and without HIV: A longitudinal study.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2025 Jan 1;266:112523. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2024.112523. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2025. PMID: 39662355
-
Sexual behavior is linked to changes in gut microbiome and systemic inflammation that lead to HIV-1 infection in men who have sex with men.Commun Biol. 2024 Sep 14;7(1):1145. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06816-z. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39277660 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic predictors for bacterial vaginosis in women living with and at risk for HIV infection.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2024 May;91(5):e13845. doi: 10.1111/aji.13845. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38720636 Free PMC article.
-
Switch to Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors During the Menopausal Transition Is Associated With Accelerated Body Composition Change in Women With HIV.Clin Infect Dis. 2025 Jun 4;80(5):1125-1132. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae540. Clin Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39495675
References
-
- Kaslow RA, Ostrow DG, Detels R, et al. The Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study: rationale, organization, and selected characteristics of the participants. Am J Epidemiol. 1987;126(2):310–318. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . HIV and older Americans. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/group/age/olderamericans/index.html. Accessed August 3, 2020.
-
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute . MACS/WIHS Combined Cohort Study. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/science/macswihs-combined-cohort-study. Accessed June 26, 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HL146205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI051519/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146208/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146192/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146242/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146193/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146241/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146333/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MD010680/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146204/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146240/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146203/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

