Exploring naphthyl derivatives as SARS-CoV papain-like protease (PLpro) inhibitors and its implications in COVID-19 drug discovery
- PMID: 33675510
- PMCID: PMC7936608
- DOI: 10.1007/s11030-021-10198-3
Exploring naphthyl derivatives as SARS-CoV papain-like protease (PLpro) inhibitors and its implications in COVID-19 drug discovery
Abstract
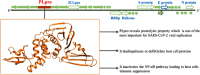
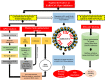
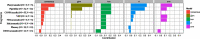
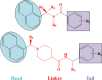
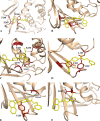
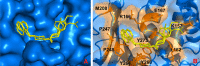
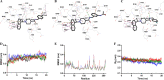
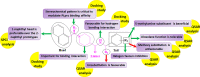
Novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) emerges as a serious threat to public health globally. The rapid spreading of COVID-19, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), proclaimed the multitude of applied research needed not only to save the human health but also for the environmental safety. As per the recent World Health Organization reports, the novel corona virus may never be wiped out completely from the world. In this connection, the inhibitors already designed against different targets of previous human coronavirus (HCoV) infections will be a great starting point for further optimization. Pinpointing biochemical events censorious to the HCoV lifecycle has provided two proteases: a papain-like protease (PLpro) and a 3C-like protease (3CLpro) enzyme essential for viral replication. In this study, naphthyl derivatives inhibiting PLpro enzyme were subjected to robust molecular modelling approaches to understand different structural fingerprints important for the inhibition. Here, we cover two main aspects such as (a) exploration of naphthyl derivatives by classification QSAR analyses to find important fingerprints that module the SARS-CoV PLpro inhibition and (b) implications of naphthyl derivatives against SARS-CoV-2 PLpro enzyme through detailed ligand-receptor interaction analysis. The modelling insights will help in the speedy design of potent broad spectrum PLpro inhibitors against infectious SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 in the future.
Keywords: COVID-19; Dynamic simulation; Molecular docking; Naphthyl derivative; SARS-CoV PLpro; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemical-informatics approach to COVID-19 drug discovery: Monte Carlo based QSAR, virtual screening and molecular docking study of some in-house molecules as papain-like protease (PLpro) inhibitors.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021 Aug;39(13):4764-4773. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1780946. Epub 2020 Jun 22. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021. PMID: 32568618 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease inhibitors through machine learning and molecular simulation approaches.Drug Discov Ther. 2025 Jul 4;19(3):189-199. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2025.01034. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Drug Discov Ther. 2025. PMID: 40571587
-
The SARS-coronavirus papain-like protease: structure, function and inhibition by designed antiviral compounds.Antiviral Res. 2015 Mar;115:21-38. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.12.015. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 25554382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial based natural compounds as potential inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like protease (PLpro): a molecular docking and dynamic simulation study.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40(24):13848-13858. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1997815. Epub 2021 Nov 3. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 34730069
-
Chalcone-amide, a privileged backbone for the design and development of selective SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Oct 5;240:114572. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114572. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35797899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Methodology-Centered Review of Molecular Modeling, Simulation, and Prediction of SARS-CoV-2.Chem Rev. 2022 Jul 13;122(13):11287-11368. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00965. Epub 2022 May 20. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 35594413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fight against novel coronavirus: A perspective of medicinal chemists.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Sep 1;201:112559. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112559. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32563814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug discovery through Covid-19 genome sequencing with siamese graph convolutional neural network.Multimed Tools Appl. 2023 May 10:1-35. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-15270-8. Online ahead of print. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023. PMID: 37362739 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro.Front Chem. 2022 Apr 26;10:876212. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.876212. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35559224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemicals as potential inhibitors for COVID-19 revealed by molecular docking, molecular dynamic simulation and DFT studies.Struct Chem. 2022;33(5):1423-1443. doi: 10.1007/s11224-022-01982-4. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Struct Chem. 2022. PMID: 35729939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re... (as accessed on 26th Nov 2020)
-
- https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (as accessed on 26th Nov 2020)
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

