Approach to the Patient Treated with Steroidogenesis Inhibitors
- PMID: 33675650
- PMCID: PMC8427736
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgab122
Approach to the Patient Treated with Steroidogenesis Inhibitors
Abstract
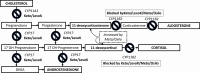
Steroidogenesis inhibitors can be given to control the hypercortisolism of Cushing's syndrome in various situations: when surgery has been unsuccessful or not possible; in metastatic adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH) or cortisol-secreting tumors; when waiting for the maximal efficacy of radiation techniques; for rapid treatment of severe hypercortisolism in patients with occult ACTH-producing tumors; or as a presurgical treatment in patients with severe comorbidities. Whilst biochemical "control" can be achieved in more than 50% of cases, daily management of such drugs can be challenging. Indeed, with a "dose-titration" or a "block and replace" approach, defining eucortisolism is usually difficult, requiring the measurement of several biological markers. Moreover, each drug has its own side effects, which must be monitored closely. The aim of this "approach to the patient" is to shed light on the management of hypercortisolism with 4 steroidogenesis inhibitors (ketoconazole, levoketoconazole, metyrapone, osilodrostat) to help endocrinologists dealing with patients with Cushing's syndrome. Various points will be discussed, such as initial dose of treatment, dose schedule, monitoring of efficacy, and side effects of monotherapy. The combination of steroidogenesis inhibitors will also be discussed.
Keywords: Cushing’s disease; Cushing’s syndrome; ectopic ACTH secretion; ketoconazole; levoketoconazole; metyrapone; osilodrostat.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Feelders RA, Newell-Price J, Pivonello R, Nieman LK, Hofland LJ, Lacroix A. Advances in the medical treatment of Cushing’s syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(4300-312. - PubMed
-
- Tritos NA. Adrenally directed medical therapies For Cushing’s syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106(1):16-25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

