Levofloxacin pharmacokinetics in saliva as measured by a mobile microvolume UV spectrophotometer among people treated for rifampicin-resistant TB in Tanzania
- PMID: 33675664
- PMCID: PMC8120342
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkab057
Levofloxacin pharmacokinetics in saliva as measured by a mobile microvolume UV spectrophotometer among people treated for rifampicin-resistant TB in Tanzania
Abstract
Background: Early detection and correction of low fluoroquinolone exposure may improve treatment of MDR-TB.
Objectives: To explore a recently developed portable, battery-powered, UV spectrophotometer for measuring levofloxacin in saliva of people treated for MDR-TB.
Methods: Patients treated with levofloxacin as part of a regimen for MDR-TB in Northern Tanzania had serum and saliva collected concurrently at 1 and 4 h after 2 weeks of observed levofloxacin administration. Saliva levofloxacin concentrations were quantified in the field via spectrophotometry, while serum was analysed at a regional laboratory using HPLC. A Bayesian population pharmacokinetics model was used to estimate the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC0-24). Subtarget exposures of levofloxacin were defined by serum AUC0-24 <80 mg·h/L. The study was registered at Clinicaltrials.gov with clinical trial identifier NCT04124055.
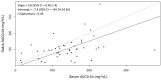
Results: Among 45 patients, 11 (25.6%) were women and 16 (37.2%) were living with HIV. Median AUC0-24 in serum was 140 (IQR = 102.4-179.09) mg·h/L and median AUC0-24 in saliva was 97.10 (IQR = 74.80-121.10) mg·h/L. A positive linear correlation was observed with serum and saliva AUC0-24, and a receiver operating characteristic curve constructed to detect serum AUC0-24 below 80 mg·h/L demonstrated excellent prediction [AUC 0.80 (95% CI = 0.62-0.94)]. Utilizing a saliva AUC0-24 cut-off of 91.6 mg·h/L, the assay was 88.9% sensitive and 69.4% specific in detecting subtarget serum AUC0-24 values, including identifying eight of nine patients below target.
Conclusions: Portable UV spectrophotometry as a point-of-care screen for subtarget levofloxacin exposure was feasible. Use for triage to other investigation or personalized dosing strategy should be tested in a randomized study.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Urine colorimetry for levofloxacin pharmacokinetics and personalized dosing in people with drug-resistant tuberculosis.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2020 Oct-Dec;9(4):411-416. doi: 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_186_20. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2020. PMID: 33323657 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Saliva as a Potential Alternative Sampling Matrix for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Levofloxacin in Patients with Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Apr 25;63(5):e02379-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02379-18. Print 2019 May. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 30782999 Free PMC article.
-
A mobile microvolume UV/visible light spectrophotometer for the measurement of levofloxacin in saliva.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Jan 19;76(2):423-429. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa420. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33089322 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic-based optimization of levofloxacin administration in the treatment of MDR-TB.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016 Oct;71(10):2691-703. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw164. Epub 2016 May 26. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27231277 Review.
-
Fluoroquinolones for the treatment of tuberculosis in children.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2015 May;95(3):229-45. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.02.037. Epub 2015 Feb 14. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2015. PMID: 25797610 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical standards for the dosing and management of TB drugs.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2022 Jun 1;26(6):483-499. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.22.0188. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2022. PMID: 35650702 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Methods for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Dose Adjustment of Tuberculosis Treatment in Clinical Settings: A Systematic Review.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2023 Mar;62(3):375-398. doi: 10.1007/s40262-023-01220-y. Epub 2023 Mar 4. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2023. PMID: 36869170 Free PMC article.
-
Can we Predict Drug Excretion into Saliva? A Systematic Review and Analysis of Physicochemical Properties.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2024 Aug;63(8):1067-1087. doi: 10.1007/s40262-024-01398-9. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2024. PMID: 39008243 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Determinants of Clinical Outcomes for Rifampin-Resistant Tuberculosis: A Multisite Prospective Cohort Study.Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Feb 8;76(3):497-505. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac511. Clin Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 35731948 Free PMC article.
-
A Call to Action: Empowering Pharmacists in Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Management.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025 Jun 17;18:3531-3544. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S517965. eCollection 2025. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025. PMID: 40546291 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2019. 2019. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/329368/9789241565714-en....
-
- WHO. Rapid Communication: Key Changes to the Treatment of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. 2019. https://www.who.int/tb/publications/2019/WHO_RapidCommunicationMDR_TB201....
-
- Bernardo J, Yew WW.. How are we creating fluoroquinolone-resistant tuberculosis? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009; 180: 288–9. - PubMed
-
- Koh W-J, Lee SH, Kang YA. et al. Comparison of levofloxacin versus moxifloxacin for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2013; 188: 858–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical